
Copernical Team
Ball Aerospace to build spacecraft for NASA Heliophysics Science Mission
 Ball Aerospace was selected to build the spacecraft for NASA's Global Lyman-alpha Imager of the Dynamic Exosphere (GLIDE) heliophysics science Mission of Opportunity. GLIDE will study variability in Earth's exosphere, the upper reaches of Earth's atmosphere where it touches space, by tracking far ultraviolet light emitted from hydrogen.
Dr. Lara Waldrop of the University of Illinois Urbana
Ball Aerospace was selected to build the spacecraft for NASA's Global Lyman-alpha Imager of the Dynamic Exosphere (GLIDE) heliophysics science Mission of Opportunity. GLIDE will study variability in Earth's exosphere, the upper reaches of Earth's atmosphere where it touches space, by tracking far ultraviolet light emitted from hydrogen.
Dr. Lara Waldrop of the University of Illinois Urbana Ozmens' SNC delivers prototype lunar crew module to DYNETICS
 Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC), the global aerospace and national security company owned by Eren and Fatih Ozmen, delivered a prototype crew module for Dynetics' Human Landing System (DHLS), to NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). Dynetics is a wholly owned subsidiary of Leidos. SNC is responsible for providing key technologies and system integration of the crew module as part of the Dynetics-led
Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC), the global aerospace and national security company owned by Eren and Fatih Ozmen, delivered a prototype crew module for Dynetics' Human Landing System (DHLS), to NASA's Johnson Space Center (JSC). Dynetics is a wholly owned subsidiary of Leidos. SNC is responsible for providing key technologies and system integration of the crew module as part of the Dynetics-led Solar system's most distant planetoid confirmed
 A team, including an astronomer from the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy (IfA), have confirmed a planetoid that is almost four times farther from the Sun than Pluto, making it the most distant object ever observed in our solar system. The planetoid, nicknamed "Farfarout," was first detected in 2018, and the team has now collected enough observations to pin down the orbit. The Minor
A team, including an astronomer from the University of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy (IfA), have confirmed a planetoid that is almost four times farther from the Sun than Pluto, making it the most distant object ever observed in our solar system. The planetoid, nicknamed "Farfarout," was first detected in 2018, and the team has now collected enough observations to pin down the orbit. The Minor China's Tianwen-1 probe enters Mars orbit: state media
 China's Tianwen-1 probe entered the orbit of the planet Mars on Wednesday, state media said, after it launched from southern China last July.
It is the latest step in Beijing's ambitious space programme, which aims to establish a crewed space station by 2022 and eventually put a man on the moon, and has opened up a new, extraterrestrial arena for US-China competition.
Tianwen-1 launched
China's Tianwen-1 probe entered the orbit of the planet Mars on Wednesday, state media said, after it launched from southern China last July.
It is the latest step in Beijing's ambitious space programme, which aims to establish a crewed space station by 2022 and eventually put a man on the moon, and has opened up a new, extraterrestrial arena for US-China competition.
Tianwen-1 launched Pollution could be one way to find an extraterrestrial civilization
 If there's an advanced extraterrestrial civilization inhabiting a nearby star system, we might be able to detect it using its own atmospheric pollution, according to new NASA research. The study looked at the presence of nitrogen dioxide gas (NO2), which on Earth is produced by burning fossil fuels but can also come from non-industrial sources such as biology, lightning, and volcanoes.
"On
If there's an advanced extraterrestrial civilization inhabiting a nearby star system, we might be able to detect it using its own atmospheric pollution, according to new NASA research. The study looked at the presence of nitrogen dioxide gas (NO2), which on Earth is produced by burning fossil fuels but can also come from non-industrial sources such as biology, lightning, and volcanoes.
"On A new method to search for potentially habitable planets
 Imaging planets orbiting around nearby stars, which could potentially harbour life, has become a possibility thanks to the progress made in observational methods by an international team of astronomers. First candidate: Alpha Centauri, a system similar to ours, "only" 4.3 light years away. This study is the subject of a publication in the journal Nature Communications.
Efforts to obtain di
Imaging planets orbiting around nearby stars, which could potentially harbour life, has become a possibility thanks to the progress made in observational methods by an international team of astronomers. First candidate: Alpha Centauri, a system similar to ours, "only" 4.3 light years away. This study is the subject of a publication in the journal Nature Communications.
Efforts to obtain di NASA Study: To Find an Extraterrestrial Civilization, Pollution Could Be the Solution
 If there’s an advanced extraterrestrial civilization inhabiting a nearby star system, we might be able to detect it using its own atmospheric pollution, according to new NASA research.
If there’s an advanced extraterrestrial civilization inhabiting a nearby star system, we might be able to detect it using its own atmospheric pollution, according to new NASA research. ExoMars discovers new gas and traces water loss on Mars
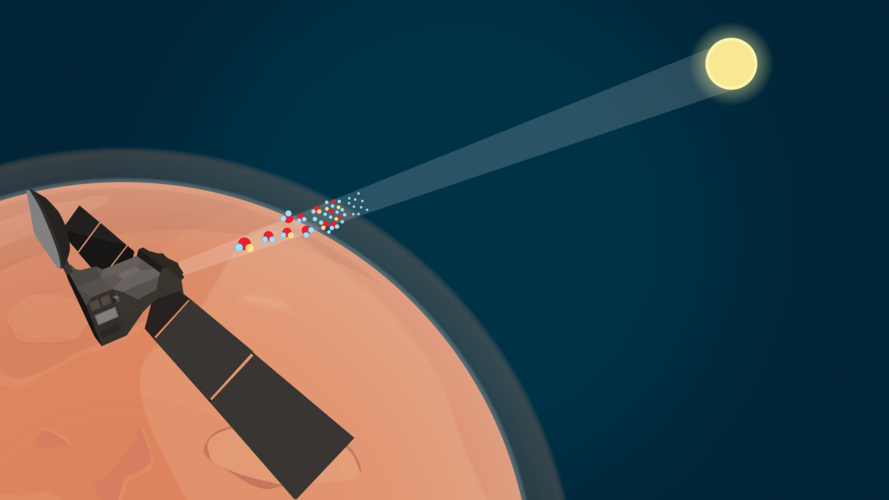
Sea salt embedded in the dusty surface of Mars and lofted into the planet’s atmosphere has led to the discovery of hydrogen chloride – the first time the ESA-Roscosmos ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter has detected a new gas. The spacecraft is also providing new information about how Mars is losing its water.
Image: Proba-V's plus one
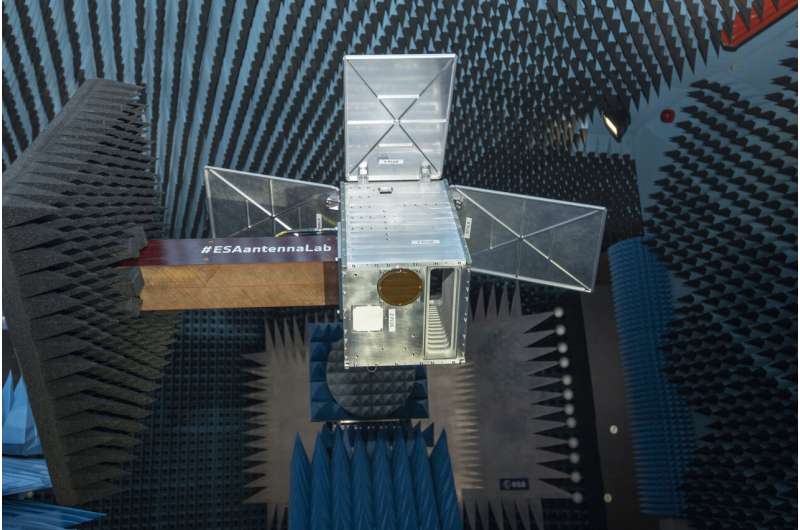

This satellite mockup, seen during antenna testing, shows the shape of ESA's new Proba-V Companion CubeSat, which is due for launch at the end of this year.
The mission is a 12-unit CubeSat—a small, low-cost satellite built up from standardized 10-cm boxes. It will fly a cut-down version of the vegetation-monitoring instrument aboard the Earth-observing Proba-V to perform experimental combined observations with its predecessor.
A pair of antennas for the CubeSat, mounted in this 'structural and thermal model' underwent testing at ESA's Compact Antenna Test Range at the ESTEC technical center in the Netherlands.
"The white patch is a directional high-data rate antenna, needed to downlink large amounts of imagery to users," explains Xavier Collaud of Aerospacelab in Belgium, developing the mission for ESA. "Then the brown patch is an omnidirectional antenna, that—combined with a similar antenna on the other side—allows the reception and transmission of lower-data rate signals in any direction, enabling the control of the mission.
"These antennnas are commercial off the shelf equipment, allowing the building up of small satellites in an affordable, modular manner.
As new probes reach Mars, here's what we know so far from trips to the red planet

Three new spacecraft are due to arrive at Mars this month, ending their seven-month journey through space.
The first, the United Arab Emirates' Hope Probe, should have made it to the red planet this week. It will stay in orbit and study its atmosphere for one complete Martian year (687 Earth days).
China's Taiwen-1 mission also enters orbit this month and will begin scouting the potential landing site for its Mars rover, due to be deployed in May.
If successful, China will become the second country to land a rover on Mars.
These two missions will join six orbiting spacecraft actively studying the red planet from above:
NASA's Mars Odyssey, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) and MAVEN OrbiterEurope's Mars ExpressIndia's Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM)the European and Russian partnership ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter.
The oldest active probe—Mars Odyssey—has been orbiting the planet for 20 years.
The third spacecraft to reach Mars this month is NASA's Perseverance rover, scheduled to land on February 18.
