
Copernical Team
Twin of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover begins terrain tests
 OPTIMISM, the full-scale engineering model of Perseverance, begins a series of rigorous tests to assess the risk of potential driving hazards on the surface of the Red Planet.
On a recent day in November, the car-size rover rolled slowly forward, then stopped, perched on the threshold of a Martian landscape. But this rover, named OPTIMISM, wasn't on the Red Planet. And the landscape was a
OPTIMISM, the full-scale engineering model of Perseverance, begins a series of rigorous tests to assess the risk of potential driving hazards on the surface of the Red Planet.
On a recent day in November, the car-size rover rolled slowly forward, then stopped, perched on the threshold of a Martian landscape. But this rover, named OPTIMISM, wasn't on the Red Planet. And the landscape was a Bezos' Blue Origin hires lobbyist after 'Space Tax' proposed
 This year, the company spent over $1.3 million on lobbying, in addition to $2 million in 2020. Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin hired Mac Campbell from Capitol Counsel - a lobbyist who had relations with the Obama administration, CBS reported. Campbell was an assistant US trade representative while working under Obama and then served as the general counsel and deputy staff director of the Senate Finance
This year, the company spent over $1.3 million on lobbying, in addition to $2 million in 2020. Jeff Bezos' Blue Origin hired Mac Campbell from Capitol Counsel - a lobbyist who had relations with the Obama administration, CBS reported. Campbell was an assistant US trade representative while working under Obama and then served as the general counsel and deputy staff director of the Senate Finance Rocket Lab signs exclusive deal to use APL space radio technologies
 Rocket Lab USA entered into an exclusive license agreement with the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) to commercialize near and deep space capable small spacecraft telemetry and control radio technology. The Frontier-S by Rocket Lab software defined radio (SDR) enables affordable communications and radio navigation for planetary and other missions beyond low Earth orbit (
Rocket Lab USA entered into an exclusive license agreement with the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) to commercialize near and deep space capable small spacecraft telemetry and control radio technology. The Frontier-S by Rocket Lab software defined radio (SDR) enables affordable communications and radio navigation for planetary and other missions beyond low Earth orbit ( NASA's Perseverance captures challenging flight by Mars Helicopter
 Video footage from NASA's Perseverance Mars rover of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter's 13th flight on Sept. 4 provides the most detailed look yet of the rotorcraft in action.
Ingenuity is currently prepping for its 16th flight, scheduled to take place no earlier than Saturday, Nov. 20, but the 160.5-second Flight 13 stands out as one of Ingenuity's most complicated.
It involved flying
Video footage from NASA's Perseverance Mars rover of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter's 13th flight on Sept. 4 provides the most detailed look yet of the rotorcraft in action.
Ingenuity is currently prepping for its 16th flight, scheduled to take place no earlier than Saturday, Nov. 20, but the 160.5-second Flight 13 stands out as one of Ingenuity's most complicated.
It involved flying Crew operations aboard Space Station return to normal
 NASA and U.S. Space Command continue to monitor the debris cloud created by a recent Russian anti-satellite test. The International Space Station and crew members are safe and have resumed normal operations.
The largest risk from the debris was in the first 24 hours and telemetry from the space station indicates no issues during that time. About 1:20 a.m. EST today, radial hatches extendin
NASA and U.S. Space Command continue to monitor the debris cloud created by a recent Russian anti-satellite test. The International Space Station and crew members are safe and have resumed normal operations.
The largest risk from the debris was in the first 24 hours and telemetry from the space station indicates no issues during that time. About 1:20 a.m. EST today, radial hatches extendin Rocket Lab launches 107th satellite; Tests helicopter recovery operations
 Rocket Lab has successfully deployed two satellites to orbit for real-time geospatial monitoring company BlackSky. Rocket Lab also successfully introduced helicopter operations to a recovery mission for the first time, using a helicopter to observe and track the Electron rocket's first stage as it descended to Earth under parachute as part of the company's program to make Electron the world's fi
Rocket Lab has successfully deployed two satellites to orbit for real-time geospatial monitoring company BlackSky. Rocket Lab also successfully introduced helicopter operations to a recovery mission for the first time, using a helicopter to observe and track the Electron rocket's first stage as it descended to Earth under parachute as part of the company's program to make Electron the world's fi Earth from Space: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
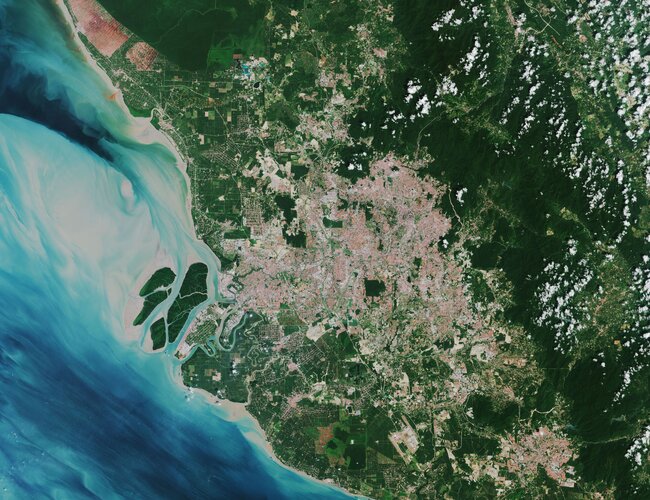
Kuala Lumpur, the capital city of Malaysia, is featured in this image captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-2 mission.
Moonshot: Japan recruits first new astronauts in 13 years

It's one small step for Japan, but one giant opportunity for would-be space cadets: the country is recruiting new astronauts for the first time in over a decade and applicants no longer have to hold a science degree.
Women are strongly encouraged to put themselves forward for the job, the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) said, as all seven of the nation's current astronauts are men.
Successful applicants, who must be Japanese, will be trained and sent on missions—potentially to the Moon, the Lunar Gateway or the International Space Station.
"We want to establish a (recruiting) system that matches the current time," JAXA's Kazuyoshi Kawasaki said at a media briefing.
"Previously we limited candidates to those with a natural science degree, but many of us agreed to make it not a requirement."
However, written exams will include university-level questions on science, technology, engineering and maths, with the applicants' English ability also tested.
JAXA said it will accept applications between December 20 and March 4—the first time it has offered positions for rookie astronauts in 13 years.
NASA: Space station remains at risk from weapons test debris

Moon lighting: partial lunar eclipse to be longest since 1440
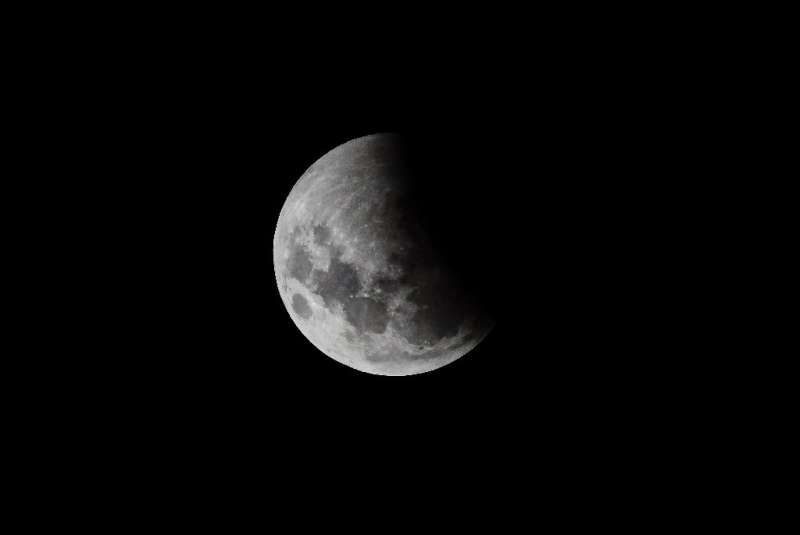

The longest partial lunar eclipse in nearly 600 years, which will bathe the Moon in red, will be visible Thursday and Friday for a big slice of humanity.
The celestial show will see the Moon almost completely cast in shadow as it moves behind the Earth, reddening 99 percent of its face.
The spectacle will be visible for all of North America, as well as parts of South America, Polynesia, Australia and northeast Asia.
Space scientists say sky-watchers in those parts who are blessed with a cloud-free view will see a slight dimming of the Moon from 0602 GMT Friday as it enters Earth's penumbra—the outer shadow.
An hour later it will appear as if someone has taken a giant bite out of the lunar disc as it starts to pass into the umbra—the full shadow.
By 0845 GMT the Moon will appear red, with the most vivid coloring visible at peak eclipse 18 minutes later.
