
Copernical Team
Bolt research effort cultivates collaboration, hypersonic workforce
 A team of scientists at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, supported by the Air Force Research Laboratory's Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFRL/AFOSR), currently leads a collaborative research and experimentation effort that could aid development of hypersonic systems.
"[Hypersonics] capability is so important [to] DOD's need to deter and defeat the U.S.'s great-power comp
A team of scientists at Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, supported by the Air Force Research Laboratory's Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFRL/AFOSR), currently leads a collaborative research and experimentation effort that could aid development of hypersonic systems.
"[Hypersonics] capability is so important [to] DOD's need to deter and defeat the U.S.'s great-power comp Planetary defenders: after NASA's DART comes ESA's Hera
 The world will be watching the milestone launch of NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test, DART, spacecraft on Wednesday, 24 November, intended to alter one small part of the Solar System forever.
DART will collide with the small moon of an asteroid in order to shift its orbit around its parent body - to test the concept of diverting threatening objects away from Earth.
ESA will pro
The world will be watching the milestone launch of NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test, DART, spacecraft on Wednesday, 24 November, intended to alter one small part of the Solar System forever.
DART will collide with the small moon of an asteroid in order to shift its orbit around its parent body - to test the concept of diverting threatening objects away from Earth.
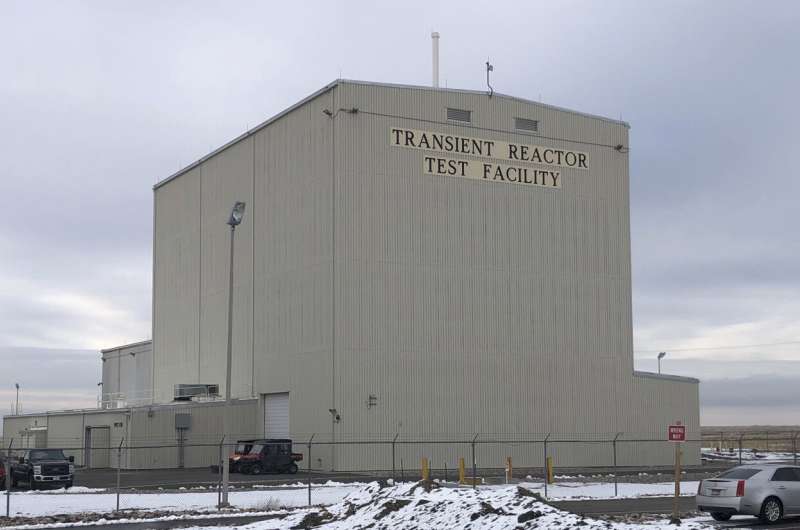
ESA will pro NASA seeks ideas for a nuclear reactor on the moon

IMM21: inflight call with ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer
 Video:
00:14:30
Video:
00:14:30
ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer talks to ESA ministers in charge of space from the International Space Station.
Japanese space tourists arrive at launch site ahead of ISS trip

Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa arrived at the Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan on Friday for training ahead of his flight to the International Space Station on a Russian-operated spacecraft.
Maezawa's mission—set for departure on December 8—will be the first to take space tourists to the ISS in over a decade.
The 45-year-old tycoon is the founder of Japan's largest online fashion mall and the country's 30th richest man, according to Forbes.
He will travel to the ISS for a 12-day mission with his assistant Yozo Hirano where Maezawa plans to document his journey for his YouTube channel.
They will travel to the orbital station in a Soyuz MS-20 spacecraft with Russian cosmonaut Alexander Misurkin.
The trio arrived at the Russia-leased cosmodrome on Friday "to complete pre-launch training", said Russia's space agency Roscosmos which has organised the flight together with US company Space Adventures.
Maezawa will be the first space tourist to travel to the ISS with Roscosmos since Canadian Guy Laliberte, co-founder of Cirque du Soleil, in 2009.
Maezawa's mission rounds off a year that has seen several space journeys completed by non-professional astronauts and more players emerging in the market.
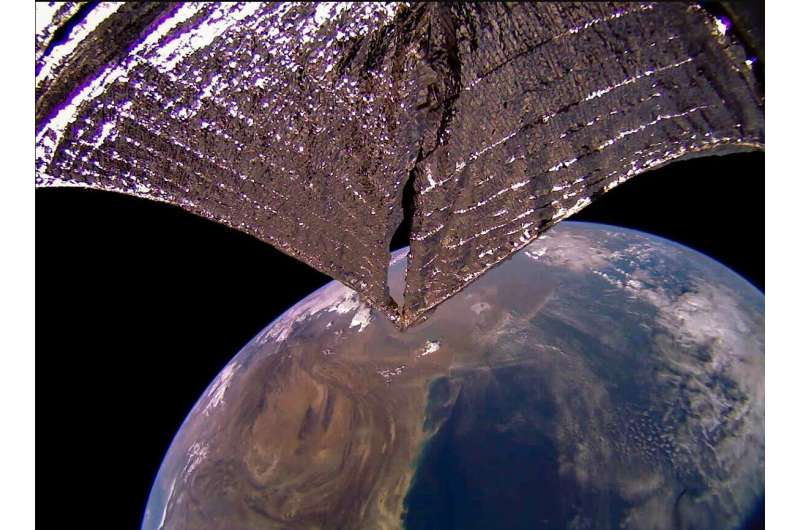
LightSail 2 has been flying for 30 months now, paving the way for future solar sail missions

Decisions from the Intermediate Ministerial Meeting 2021
Press Release N° 39–2021
Government ministers in charge of space activities in ESA’s Member States today met at an Intermediate Ministerial Meeting held in Matosinhos, Portugal.
The Council of Ministers unanimously adopted a Resolution to accelerate the use of space in Europe (the “Matosinhos manifesto”) to tackle the urgent and unprecedented societal, economic and security challenges faced by Europe and its citizens.
Week in images: 15 - 19 November 2021
Week in images: 15 - 19 November 2021
Discover our week through the lens
Rocky roads through Lanzarote
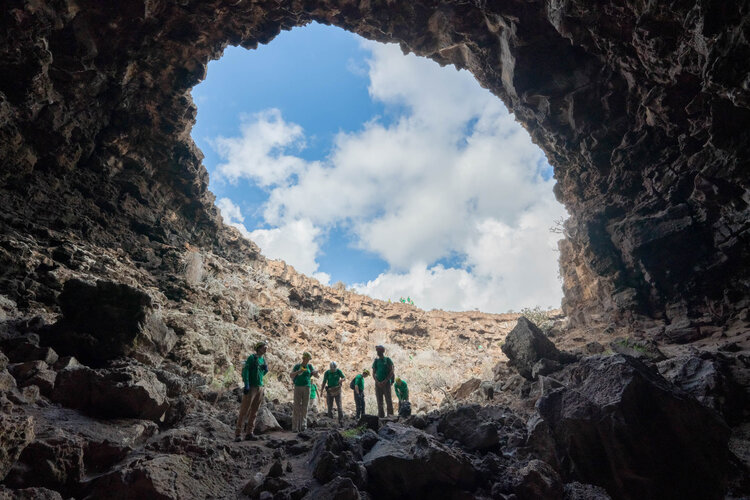 Image:
Image:
Take away the clouds, bulk up the humans with suits and add an orange-red filter and this could be an image from a future mission to Mars.
The actual site, the Corona lava tube in Lanzarote, Spain, is closer than one might think to the Red Planet.
That’s why participants of ESA’s Pangaea course came here this week for the third session of their planetary geology training.
ESA astronaut Andreas Mogensen, ESA engineer Robin Eccleston and NASA astronaut Kathleen Rubins are this year’s students learning from geologists how to best explore the Moon and Mars right here on Earth.
Before ending up in
Space dust presents opportunities, challenges as Parker Solar Probe speeds towards Sun
 Propelled by a recent swing past Venus, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is healthy and performing normally as it heads toward its next closest approach to the Sun on Nov. 21.
Parker Solar Probe will break its own distance and speed records on that approach - the 10th of 24 planned, progressively closer trips around the Sun - when it comes about 5.3 million miles (8.5 million kilometers) from the
Propelled by a recent swing past Venus, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is healthy and performing normally as it heads toward its next closest approach to the Sun on Nov. 21.
Parker Solar Probe will break its own distance and speed records on that approach - the 10th of 24 planned, progressively closer trips around the Sun - when it comes about 5.3 million miles (8.5 million kilometers) from the 