
Copernical Team
European space firm to build small, reusable launcher
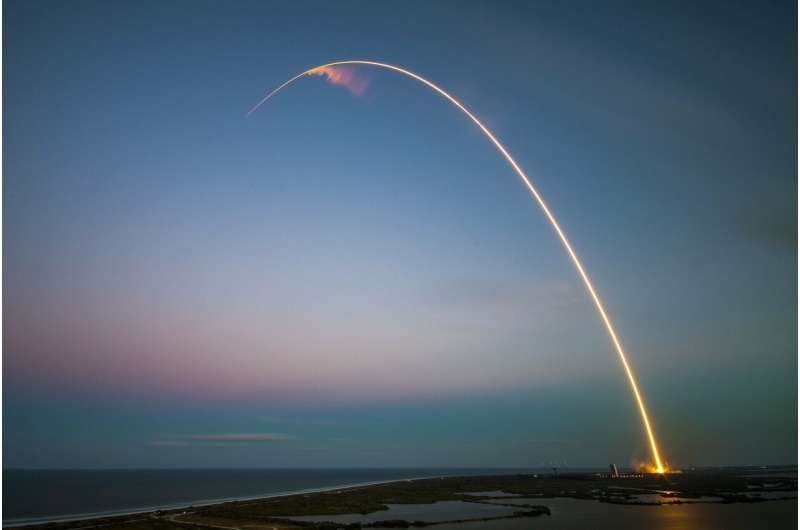

European space firm ArianeGroup will develop a small, reusable carrier rocket to compete with SpaceX, the pioneer of the technology, France's economy minister said Monday.
The launch vehicle should be operational by 2026, Bruno Le Maire said in a visit to ArianeGroup's large rocket testing facility in Vernon, northwest France.
Le Maire admitted that Europe was "behind the curve on reusable launchers".
"We didn't believe in it. We fell behind our American partners who developed Space X and Falcon 9, and we must narrow the gap," he said.
Elon Musk's SpaceX has become a major leader in the sector, with its rockets taking satellites and astronauts into orbit.
Explore further
© 2021 AFP
Webb moved for fuelling
 Video:
00:00:51
Video:
00:00:51
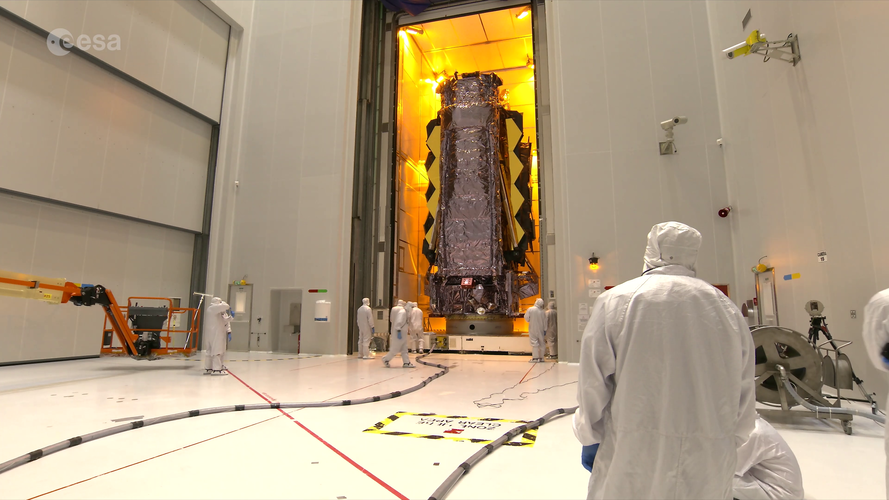
The James Webb Space Telescope, configured for flight, was moved from the cleanroom to the payload preparation facility for fuelling at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana on 11–12 November 2021.
Webb will be loaded with propellants before being mounted on top of the rocket and then encapsulated by the Ariane 5 fairing.
Webb will be the largest, most powerful telescope ever launched into space. As part of an international collaboration agreement, ESA is providing the telescope’s launch service using the Ariane 5 launch vehicle. Working with partners, ESA was responsible for the development and qualification
Webb fuelled for launch
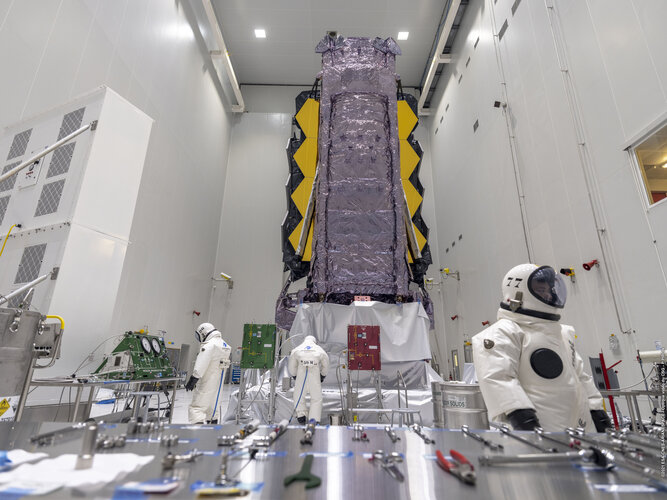 Image:
Webb fuelled for launch
Image:
Webb fuelled for launch ESA spurs 5G digital connectivity
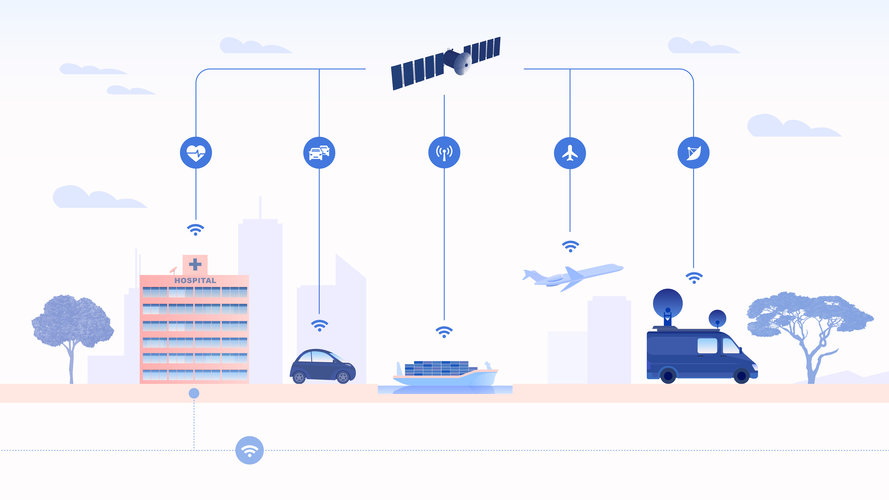
Efforts to enable seamless connectivity and reduce the digital divide by using telecommunications satellites to enhance terrestrial 5G services have leapt forward.
Russia to send Japanese tycoon to ISS in return to space tourism
 Russia on Wednesday will send Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa to the International Space Station in a move marking Moscow's return to the now booming space tourism business after a decade-long break.
One of Japan's richest men, Maezawa, 46, will blast off from the Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan accompanied by his assistant Yozo Hirano.
On Sunday morning, their Soyuz spacecraft wi
Russia on Wednesday will send Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa to the International Space Station in a move marking Moscow's return to the now booming space tourism business after a decade-long break.
One of Japan's richest men, Maezawa, 46, will blast off from the Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan accompanied by his assistant Yozo Hirano.
On Sunday morning, their Soyuz spacecraft wi Yusaku Maezawa: irreverent billionaire fascinated by space
 Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa, who blasts off for the International Space Station this week, is an irreverent space enthusiast who has made headlines for splashing the cash on modern art.
The 46-year-old tycoon is the founder of Japan's largest online fashion mall and is the country's 30th-richest person, according to business magazine Forbes.
But he is far from the traditional ima
Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa, who blasts off for the International Space Station this week, is an irreverent space enthusiast who has made headlines for splashing the cash on modern art.
The 46-year-old tycoon is the founder of Japan's largest online fashion mall and is the country's 30th-richest person, according to business magazine Forbes.
But he is far from the traditional ima Two new satellites mark further enlargement of Galileo
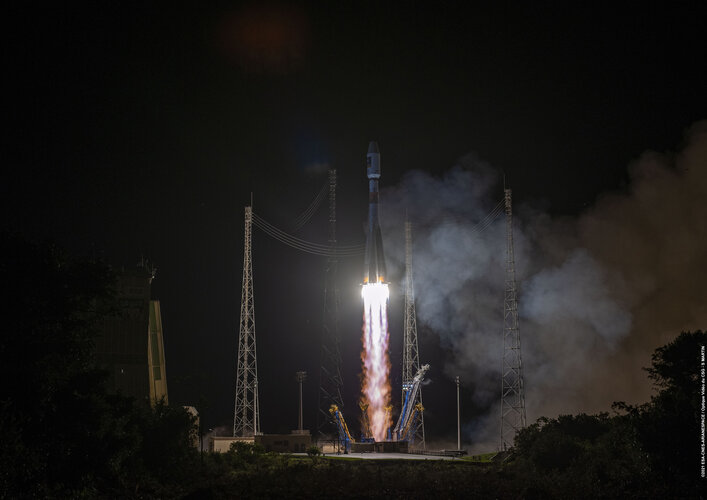

Europe’s largest satellite constellation has grown even bigger, following the launch of two more Galileo navigation satellites by Soyuz launcher from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana on 5 December. Galileo satellites 27-28 add to an existing 26-satellite constellation in orbit, providing the world’s most precise satnav positioning to more than 2.3 billion users around the globe.
TESS discovers a planet the size of Mars but with the makeup of Mercury
 Ultra-short-period planets are small, compact worlds that whip around their stars at close range, completing an orbit - and a single, scorching year - in less than 24 hours. How these planets came to be in such extreme configurations is one of the continuing mysteries of exoplanetary science.
Now, astronomers have discovered an ultra-short-period planet (USP) that is also super light. The
Ultra-short-period planets are small, compact worlds that whip around their stars at close range, completing an orbit - and a single, scorching year - in less than 24 hours. How these planets came to be in such extreme configurations is one of the continuing mysteries of exoplanetary science.
Now, astronomers have discovered an ultra-short-period planet (USP) that is also super light. The Lunar radar data uncovers new clues about moon's ancient past
 The dusty surface of the moon - immortalized in images of Apollo astronauts' lunar footprints - formed as the result of asteroid impacts and the harsh environment of space breaking down rock over millions of years. An ancient layer of this material, covered by periodic lava flows and now buried under the lunar surface, could provide new insight into the Moon's deep past, according to a team of s
The dusty surface of the moon - immortalized in images of Apollo astronauts' lunar footprints - formed as the result of asteroid impacts and the harsh environment of space breaking down rock over millions of years. An ancient layer of this material, covered by periodic lava flows and now buried under the lunar surface, could provide new insight into the Moon's deep past, according to a team of s High-Speed Lunar Surface Transportation
 Proposed lunar surface mobility systems for human colonization appear to be severely limited in speed and payload capabilities. Roving vehicles are massive and move slowly over the rough lunar terrain, at a high cost of energy and life support supplies.
Flying units, powered by chemical rockets are fast, but the price of speed is payload and range. On the other hand, a hopping transporter
Proposed lunar surface mobility systems for human colonization appear to be severely limited in speed and payload capabilities. Roving vehicles are massive and move slowly over the rough lunar terrain, at a high cost of energy and life support supplies.
Flying units, powered by chemical rockets are fast, but the price of speed is payload and range. On the other hand, a hopping transporter 