
Copernical Team
US Space Force releases decades of Bolide Data to NASA for Planetary Defense Studies
 An agreement between NASA and the U.S. Space Force recently authorized the public release of decades of data collected by U.S. government sensors on fireball events (large bright meteors also known as bolides) for the benefit of the scientific and planetary defense communities. This action results from collaboration between NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO) and the U.S. Space F
An agreement between NASA and the U.S. Space Force recently authorized the public release of decades of data collected by U.S. government sensors on fireball events (large bright meteors also known as bolides) for the benefit of the scientific and planetary defense communities. This action results from collaboration between NASA's Planetary Defense Coordination Office (PDCO) and the U.S. Space F 'Moon landing' performed with DLR Robotic Motion Simulator
 How will astronauts land safely on the Moon in the future? A seamless interaction between pilot and spacecraft is crucial to ensuring a successful Moon landing. Together with partners from industry and research, the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) has conducted a special experiment. European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut and test pilot Roberto Vittori has
How will astronauts land safely on the Moon in the future? A seamless interaction between pilot and spacecraft is crucial to ensuring a successful Moon landing. Together with partners from industry and research, the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum fur Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) has conducted a special experiment. European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut and test pilot Roberto Vittori has Virgin Orbit to launch maritime data satellite from the UK
 Virgin Orbit has announced an agreement with The Satellite Applications Catapult (The Catapult) to launch the latest satellite in The Catapult's In-Orbit Demonstration (IOD) programme into space from the UK later this year.
The satellite, called Amber-1, is a partnership between The Catapult and Horizon Technologies. Built by AAC Clyde Space in Scotland, it will be launched by Virgin Orbit
Virgin Orbit has announced an agreement with The Satellite Applications Catapult (The Catapult) to launch the latest satellite in The Catapult's In-Orbit Demonstration (IOD) programme into space from the UK later this year.
The satellite, called Amber-1, is a partnership between The Catapult and Horizon Technologies. Built by AAC Clyde Space in Scotland, it will be launched by Virgin Orbit NASA's Curiosity Mars rover reroutes away from 'Gator-Back' rocks
 NASA's Curiosity Mars rover spent most of March climbing the "Greenheugh Pediment" - a gentle slope capped by rubbly sandstone. The rover briefly summited this feature's north face two years ago; now on the pediment's southern side, Curiosity has navigated back onto the pediment to explore it more fully.
But on March 18, the mission team saw an unexpected terrain change ahead and realized
NASA's Curiosity Mars rover spent most of March climbing the "Greenheugh Pediment" - a gentle slope capped by rubbly sandstone. The rover briefly summited this feature's north face two years ago; now on the pediment's southern side, Curiosity has navigated back onto the pediment to explore it more fully.
But on March 18, the mission team saw an unexpected terrain change ahead and realized First private mission readies for launch to ISS
 The first fully private mission to the International Space Station is set to blast off Friday with a four-member crew from startup company Axiom Space.
The partnership has been hailed by NASA, which sees it as a key step in its goal to commercialize the region of space known as "low Earth orbit," leaving the agency to focus on more ambitious endeavors deeper into the cosmos.
Takeoff is s
The first fully private mission to the International Space Station is set to blast off Friday with a four-member crew from startup company Axiom Space.
The partnership has been hailed by NASA, which sees it as a key step in its goal to commercialize the region of space known as "low Earth orbit," leaving the agency to focus on more ambitious endeavors deeper into the cosmos.
Takeoff is s Ride into orbit secured for Copernicus Sentinel-1C

A contract signed with Arianespace secures the launch for the third Copernicus Sentinel-1 satellite. Scheduled to lift off on ESA’s new Vega-C rocket from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana in the first half of 2023, Sentinel-1C will continue the critical task of delivering key radar imagery for a wide range of services, applications and science – all of which benefit society.
Curiosity Mars Rover reroutes away from 'gator-back' rocks

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover spent most of March climbing the "Greenheugh Pediment"—a gentle slope capped by rubbly sandstone. The rover briefly summited this feature's north face two years ago; now on the pediment's southern side, Curiosity has navigated back onto the pediment to explore it more fully.
Webb telescope's cool view on how stars, planets form
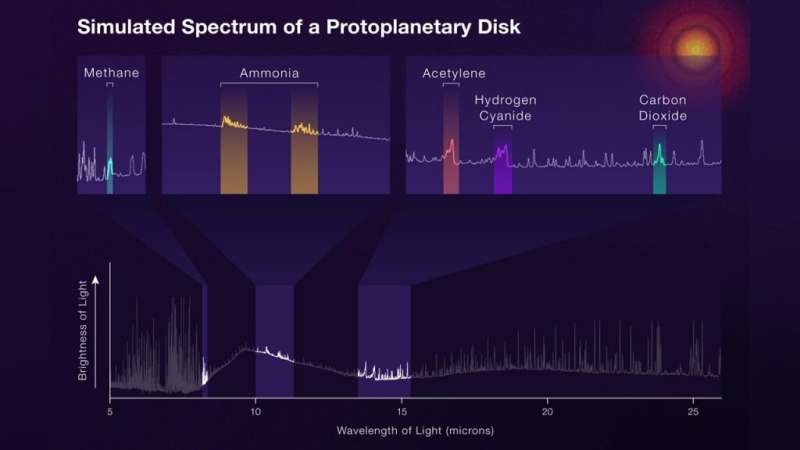
The ongoing success of the multi-instrument optics alignment for NASA's Webb telescope's near-infrared instruments has moved the attention of the commissioning team to chill as we carefully monitor the cooling of the Mid-InfraRed Instrument (MIRI) down to its final operating temperature of less than 7 kelvins (-447 degrees Fahrenheit, or -266 degrees Celsius). We are continuing other activities during this slow cooldown which include monitoring the near-infrared instruments. As MIRI cools, other major components of the observatory, such as the backplane and mirrors, also continue to cool and are approaching their operational temperatures.
Eye on world health
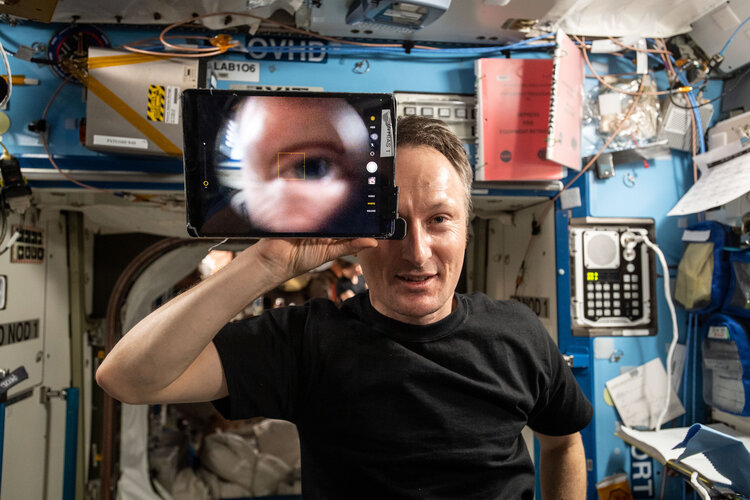 Image:
Image:
H a p p y W o r l d H e a l t h D a y
Celebrated each year on 7 April, World Health Day shines a light on a health topic of concern. This year all eyes, including ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer’s, are on the health of our planet Earth.
From on board the International Space Station 400 km above Earth, Matthias has a unique overview of our planet. Beautiful yet fragile, resilient yet under threat, our third rock from the Sun nevertheless needs looking after.
Matthias work in space during Cosmic Kiss reinforces this. Besides taking numerous
Living Planet Fellowship: Call for Proposals
Living Planet Fellowship: Call for Proposals
