
Copernical Team
University of Zurich and Airbus grow miniature human tissue on the International Space Station ISS
 With the next supply flight to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Hub of the University of Zurich (UZH) and Airbus Defence and Space are bringing an experiment into space, which is intended to further advance the industrial production of human tissue in zero-gravity conditions. With this step, space could become a workshop for producing miniature human tissue for terrestrial use in
With the next supply flight to the International Space Station (ISS), the Space Hub of the University of Zurich (UZH) and Airbus Defence and Space are bringing an experiment into space, which is intended to further advance the industrial production of human tissue in zero-gravity conditions. With this step, space could become a workshop for producing miniature human tissue for terrestrial use in KyotoU to test slats of wood aboard Japan's Kibo platform on the ISS
 Humans have relied on forests and trees - for shelter, food, and fuel - from the earliest times. As technology has advanced, timber has been utilized for buildings, ships, and railroads. And now we may be on the verge of taking wood into space.
Why wood? Building in space with futuristic, 'space-age' materials might seem to be the obvious choice: lumber's fragility and combustibility might
Humans have relied on forests and trees - for shelter, food, and fuel - from the earliest times. As technology has advanced, timber has been utilized for buildings, ships, and railroads. And now we may be on the verge of taking wood into space.
Why wood? Building in space with futuristic, 'space-age' materials might seem to be the obvious choice: lumber's fragility and combustibility might First light from Sunstorm CubeSat
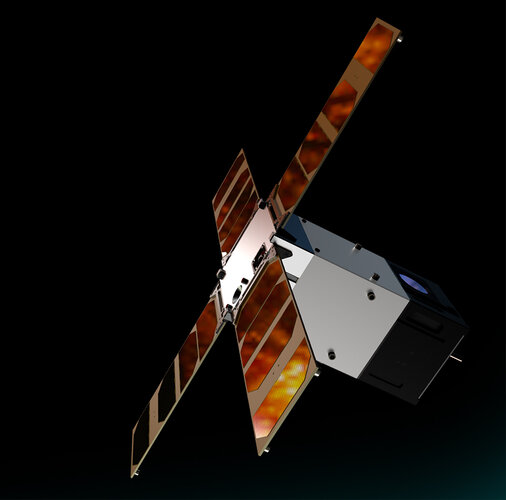 Image:
First light from Sunstorm CubeSat
Image:
First light from Sunstorm CubeSat Maine museum to host large chunk of Mars rock

A Maine museum will play host to a chunk of rock it said is the largest intact Mars rock on Earth.
The Maine Mineral & Gem Museum said the specimen weighs 32 pounds (15 kilograms) and is about 10 inches (25 centimeters) at its longest point. The museum said the rock was the result of an asteroid impact on the surface of Mars that ejected material into an Earth-crossing orbit in space.
There are less than 500 pounds (227 kilograms) of Mars rock known to exist on Earth, the museum said.
The rock is known as "Taoudenni 002." The Bethel, Maine, museum said it will include the rock when it opens to the public on Sept. 1.
The museum said it is planning a reception with limited capacity on Aug. 31 to celebrate the acquisition of the rock. Two scientists from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration are expected to attend, the museum said.
Explore further
© 2021 The Associated Press. All rights reserved.
Space: The wooden frontier
Humans have relied on forests and trees—for shelter, food, and fuel—from the earliest times. As technology has advanced, timber has been utilized for buildings, ships, and railroads. And now we may be on the verge of taking wood into space.
Why wood? Building in space with futuristic, 'space-age' materials might seem to be the obvious choice: lumber's fragility and combustibility might seem counter-intuitive by comparison.
Therein lies the rationale for wood: as a natural, economical, carbon-based material, its production is considerably more sustainable than advanced alternatives, and its disposal—especially when dropped from orbit into the upper atmosphere—is complete and without harmful byproducts.
Moreover, earlier investigations—in earth-bound labs—have demonstrated wood's surprising ability to withstand a wide range of temperatures, from -150 to 150 degrees Celsius.
Fire ravages Esrange Space Centre in northern Sweden
A large fire tore through a scientific space research centre in northern Sweden on Thursday, destroying part of the rocket launch pad, officials said.
The fire broke out early Thursday "during a scheduled static firing test of a solid rocket motor" and was under control by late afternoon when "post-extinguishing work" was being conducted, Esrange Space Centre said in a statement.
Located in the town of Kiruna, the centre is a base for scientific research with high-altitude balloons, studies on the aurora borealis phenomenon (also known as the Northern Lights), sounding rocket launches and satellite tracking, among other things.
No injuries were reported, though some staff were taken to hospital for a check-up.
The fire damaged "part of the sounding rocket launching infrastructure", Esrange Space Centre said.
"The full extent of damages and consequences for launching operations cannot yet be assessed," it said.
Explore further
© 2021 AFP
Blue Origin launches artwork, moon-landing test into space
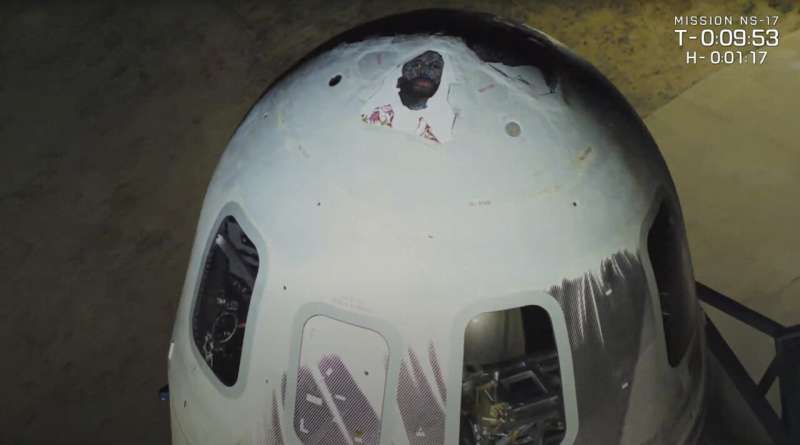

Blue Origin launched artwork painted on a capsule and a moon-landing navigation experiment into space Thursday, a month after sending founder Jeff Bezos on the company's first passenger flight.
No one was aboard for Thursday's 10-minute flight, which included other experiments from NASA and others.
The paintings by Ghana artist Amoako Boafo were on three parachute panels on the outside of the capsule at the very top. Boafo painted a self-portrait as well as portraits of his mother and a friend's mother, explaining "a mother's love comes from a place that is out of this world," said Blue Origin launch commentator Kiah Erlich, a company official.
Engineers test liquid acquisition device aboard Blue Origin's New Shepard rocket
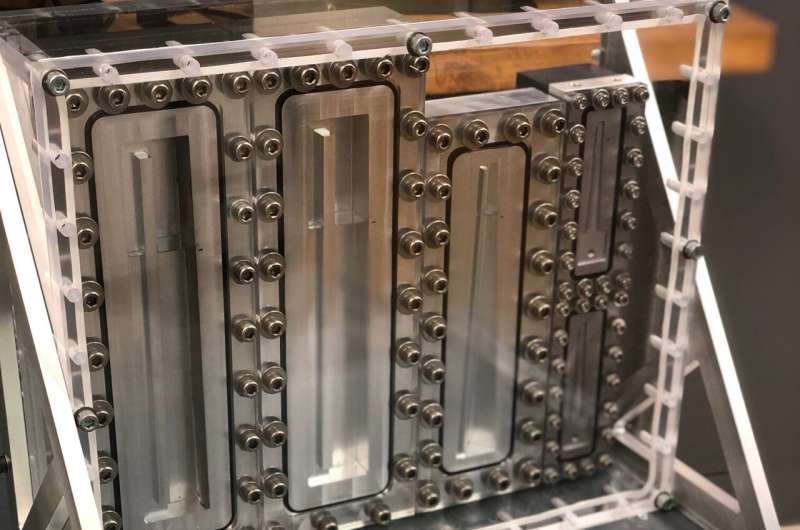

A Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) experiment was performed aboard Blue Origin's New Shepard suborbital rocket today, which launched from Van Horn, Texas. Five variations of the tapered liquid acquisition device (LAD), which is designed to safely deliver liquid propellant to a rocket engine from fuel tanks, were aboard the rocket to evaluate their performance in microgravity.
Manned Mars mission viable if it doesn't exceed four years, concludes international research team

Sending human travelers to Mars would require scientists and engineers to overcome a range of technological and safety obstacles. One of them is the grave risk posed by particle radiation from the sun, distant stars and galaxies.
Answering two key questions would go a long way toward overcoming that hurdle: Would particle radiation pose too grave a threat to human life throughout a round trip to the red planet? And, could the very timing of a mission to Mars help shield astronauts and the spacecraft from the radiation?
Experiment to grow miniature human tissue on the International Space Station

The process for the joint 3D Organoids in Space project originated from the University of Zurich (UZH) researchers Oliver Ullrich and Cora Thiel. Together with Airbus, the two pioneers in research on how gravity affects and regulates human cells have developed the process to project maturity. The Airbus Innovations team led by project manager Julian Raatschen has developed the hardware and is providing access to the International Space Station (ISS). It took the project partners only three years from idea to the first production test in space. During this time, they completed various test phases and overcame highly competitive internal selection processes.
