
Copernical Team
Student-designed experiment to measure Earth's magnetic field arrives at Space Station
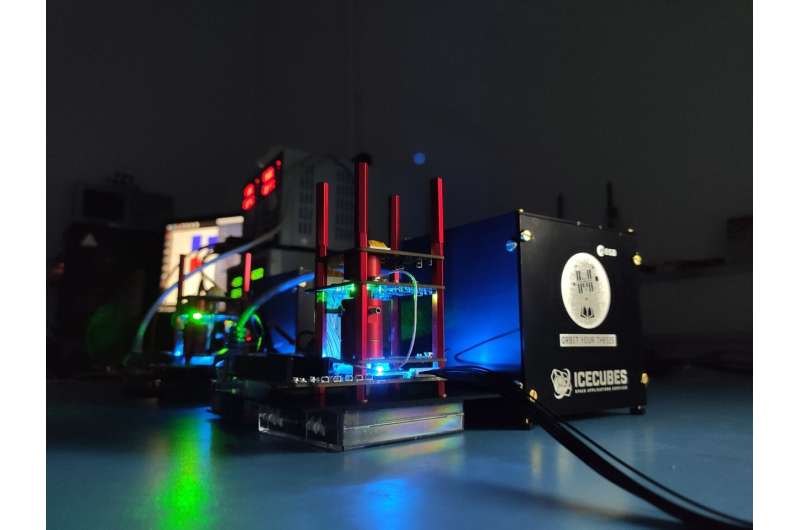

Oscar-Qube, short for Optical Sensors based on CARbon materials: QUantum Belgium, is an experiment developed by a group of students from the University of Hasselt, Belgium. Part of ESA Education Office's Orbit Your Thesis! program, the experiment arrived at the International Space Station on Space X Dragon CR23 resupply mission yesterday.
This week, ESA astronaut Thomas Pesquet will install the experiment in the Ice Cubes Facility that offers commercial and educational access to the microgravity environment of the Space Station.
Oscar-Qube's mission is to create a detailed map of Earth's magnetic field. It makes use of a new type of magnetometer that exploits diamond-based quantum sensing, meaning that it is highly sensitive, offers measurements to the nano scale, and has a better than 100-nanosecond response time.
These features combine to create a powerful experiment that, once in position, will allow it to map the Earth's magnetic field to an unrivaled level of precision.
Oscar-Qube is designed and built exclusively by the first student team to test a diamond-based quantum technology sensing device in space. They will go on to manage operations during its 10-month stay onboard the International Space Station.
ESA and UN offer worldwide access to hypergravity testing
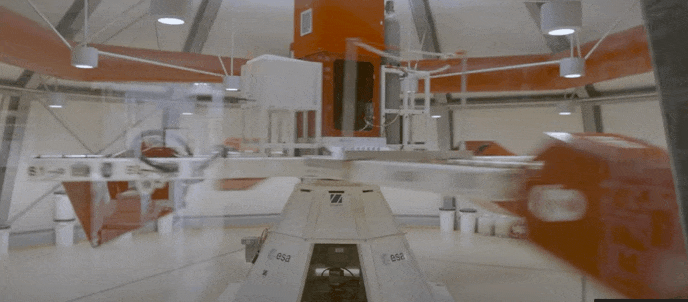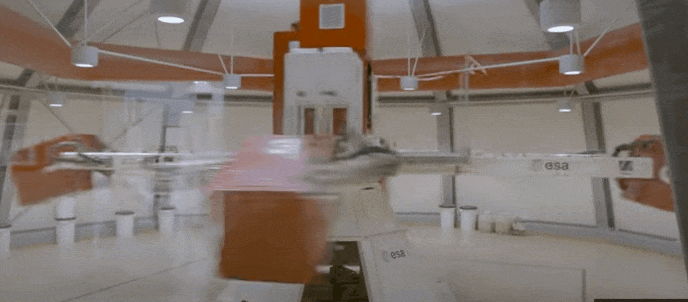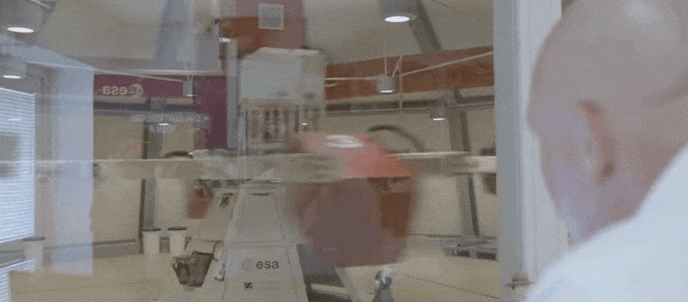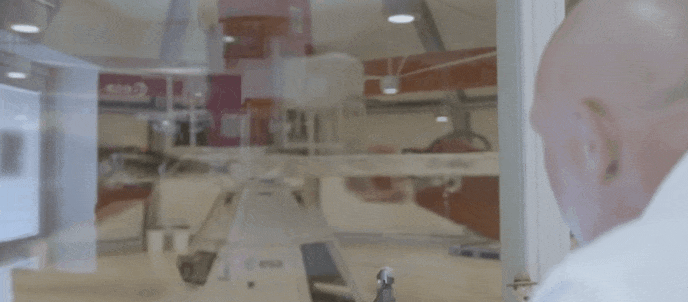
ESA and the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs are opening the second round of their HyperGES fellowship, part of the Access to Space For All Initiative, offering student teams around the globe the chance to perform hypergravity experiments using the Large Diameter Centrifuge at ESA’s ESTEC technical centre in the Netherlands, with a particular focus on developing nations.
China wants to build a spaceship that's kilometers long

It's no secret that China has become a major contender in spaceflight. In the past 20 years, the China National Space Agency (CNSA) has accomplished some historic firsts. This includes sending astronauts to space, deploying three space stations (as part of the Tiangong program), developing heavy launch vehicles (like the Long March 5), and sending robotic explorers to the far side of the moon and Mars.
Looking ahead to the next decade and beyond, China is planning on taking even bolder steps to develop its space program. Among the many proposals the country's leaders are considering for its latest five-year plan, one involved creating an "ultra-large spacecraft spanning kilometers." Having this spacecraft in low Earth orbit (LEO) would be a game-changer for China, allowing for long-duration missions and the use of space resources.
Cold planets exist throughout our Galaxy, even in the Galactic bulge
 Although thousands of planets have been discovered in the Milky Way, most reside less than a few thousand light years from Earth. Yet our Galaxy is more than 100,000 light years across, making it difficult to investigate the Galactic distribution of planets. But now, a research team has found a way to overcome this hurdle.
In a study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, research
Although thousands of planets have been discovered in the Milky Way, most reside less than a few thousand light years from Earth. Yet our Galaxy is more than 100,000 light years across, making it difficult to investigate the Galactic distribution of planets. But now, a research team has found a way to overcome this hurdle.
In a study published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, research Promising candidates revealed for next-generation LED-based data communications
 A new paper from the University of Surrey and the University of Cambridge has detailed how two relatively unexplored semiconducting materials can satisfy the telecommunication industry's hunger for enormous amounts of data at ever-greater speeds.
Light-emitting diode (LED)-based communications techniques allow computing devices, including mobile phones, to communicate with one another by u
A new paper from the University of Surrey and the University of Cambridge has detailed how two relatively unexplored semiconducting materials can satisfy the telecommunication industry's hunger for enormous amounts of data at ever-greater speeds.
Light-emitting diode (LED)-based communications techniques allow computing devices, including mobile phones, to communicate with one another by u 3D-printed lunar floor
 Image:
3D-printed lunar floor
Image:
3D-printed lunar floor A Lunar-based Soft X-ray Imager for the Earth's magnetosphere
 The solar wind-magnetosphere coupling and its dynamic process are the basic driving factors for space weather. To understand its physical connotation, it is necessary to understand the processes of global scale responses, mass and energy transportation, and the coupling between different regions.
However, relying on single-point or multi-point in-situ measurements is not enough for graspin
The solar wind-magnetosphere coupling and its dynamic process are the basic driving factors for space weather. To understand its physical connotation, it is necessary to understand the processes of global scale responses, mass and energy transportation, and the coupling between different regions.
However, relying on single-point or multi-point in-situ measurements is not enough for graspin Roscosmos offered ESA extended use of Soyuz In French Guiana
 Russian space agency Roscosmos has offered the European Space Agency (ESA) to continue using Russia's Soyuz carrier rockets from the Kourou spaceport in French Guiana for different payloads, and the talks are ongoing, ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher told Sputnik.
"The extended use of Soyuz is one of the topics we're considering right now. In fact, I have discussed it with Mr. [Dmitry
Russian space agency Roscosmos has offered the European Space Agency (ESA) to continue using Russia's Soyuz carrier rockets from the Kourou spaceport in French Guiana for different payloads, and the talks are ongoing, ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher told Sputnik.
"The extended use of Soyuz is one of the topics we're considering right now. In fact, I have discussed it with Mr. [Dmitry World-leading space venture capital firm announces idea-stage incubator
 SpaceFund has announced at the North American Space Summit, the formation of its SpaceFund Labs idea incubator. The goal of this new division of SpaceFund is to capture and turn exciting ideas into funded businesses by creating a unique incubation plan for each idea that is accepted into the program.
"SpaceFund Labs is about discovering and nurturing the most brilliant ideas in AI, biotech
SpaceFund has announced at the North American Space Summit, the formation of its SpaceFund Labs idea incubator. The goal of this new division of SpaceFund is to capture and turn exciting ideas into funded businesses by creating a unique incubation plan for each idea that is accepted into the program.
"SpaceFund Labs is about discovering and nurturing the most brilliant ideas in AI, biotech Spacecraft deorbiting device developed at Purdue ready for upcoming test launch
 A drag sail that a team at Purdue University developed to pull launch vehicles in space back to Earth is scheduled to undergo a test launch on Thursday (Sept. 2).
The mission, set to take off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, will evaluate how well the prototype helps its vehicle deorbit from space after mission completion. A livestream of the launch will be available through
A drag sail that a team at Purdue University developed to pull launch vehicles in space back to Earth is scheduled to undergo a test launch on Thursday (Sept. 2).
The mission, set to take off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, will evaluate how well the prototype helps its vehicle deorbit from space after mission completion. A livestream of the launch will be available through 