Copernical Team
Dragon delivery: European science destined for space
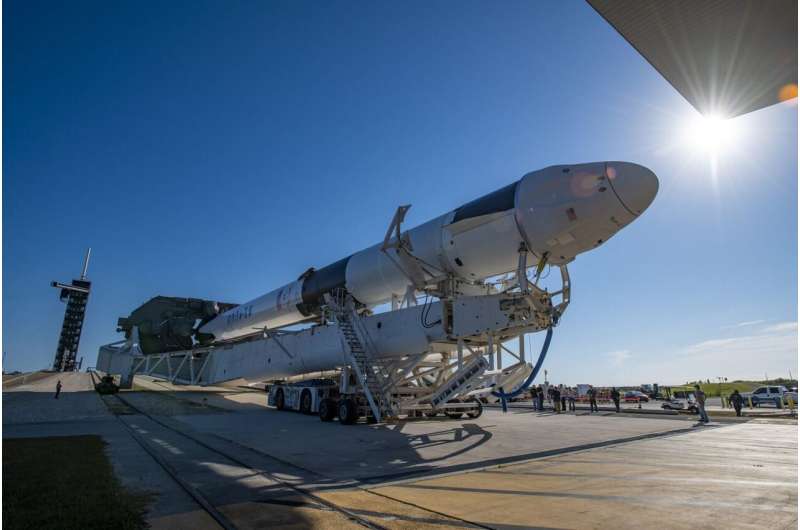

The next SpaceX resupply vehicle is packed with European science, ready for delivery to the International Space Station just in time for Christmas.
The Dragon spacecraft is scheduled to launch from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, U.S., at 11:06 CET (10:06 GMT) Tuesday 21 December. But before it does, we take a quick peek at some of the European cargo it carries.
Safe air
Astronauts living on the International Space Station never get a breath of fresh outdoor air.
In their closed atmosphere, irritating, poisonous and carcinogenic gas compounds emanate from materials, equipment and the crew itself. However, there is no window to open to freshen the room, so the astronauts must rely on the air revitalisation system.
Air quality is monitored continuously to assure the crew's health and well-being. A rapid response by the astronauts to any accidental release of harmful gaseous contaminants, or malfunction of the air system is essential, and air monitoring is even more important as missions last longer and samples cannot be taken to Earth for analysis.
Science fiction revisited: Ramjet propulsion
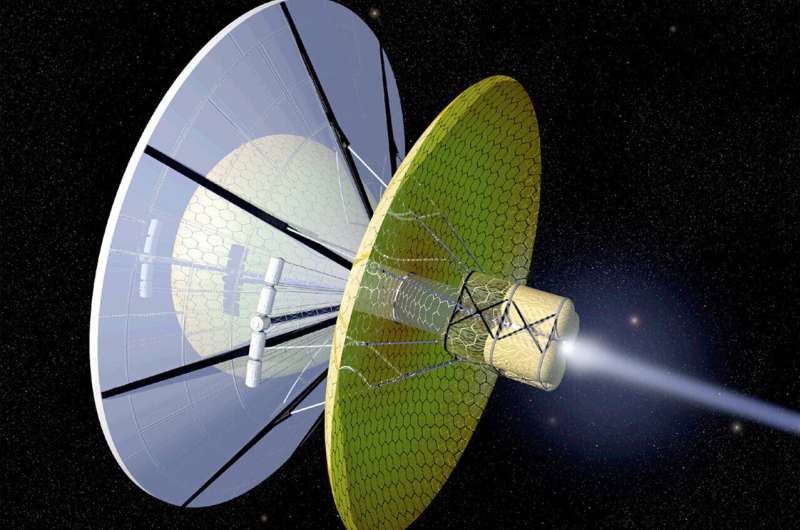

In science fiction stories about contact with extraterrestrial civilisations, there is a problem: What kind of propulsion system could make it possible to bridge the enormous distances between the stars? It cannot be done with ordinary rockets like those used to travel to the moon or Mars. Many more or less speculative ideas about this have been put forward—one of them is the "Bussard collector" or "Ramjet propulsion". It involves capturing protons in interstellar space and then using them for a nuclear fusion reactor.
Peter Schattschneider, physicist and science fiction author, has now analyzed this concept in more detail together with his colleague Albert Jackson from the USA. The result is unfortunately disappointing for fans of interstellar travel: it cannot work the way Robert Bussard, the inventor of this propulsion system, thought it up in 1960. The analysis has now been published in the scientific journal Acta Astronautica.
The hydrogen-collecting machine
"The idea is definitely worth investigating," says Prof. Peter Schattschneider. "In interstellar space there is highly diluted gas, mainly hydrogen—about one atom per cubic centimeter.
NASA says glitch on Boeing rocket delays launch again

NASA plans to replace an engine controller aboard its massive SLS rocket after finding a communications glitch with the system's avionics during preflight testing, the latest setback in a program for which Boeing Co. is the main contractor and that has been plagued by years of delays and billions of dollars in costs beyond its initial budget.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration also said Friday it will explore launch dates for a test flight in March and April.
The rocket, which Congress authorized and began funding in 2010, was supposed to fly in late 2016. In October, NASA solicited ideas from the aerospace industry about ways to lower the costs associated with the Space Launch System.
Replacing the unit on one of the SLS's four RS-25 engines is "the best course of action," the agency said. The update comes after engineers preparing the rocket for flight detected a communications problem last month between the rocket's avionics system and the No. 4 engine, and began troubleshooting the issue.
NASA plans to use the Space Launch System rocket and Orion crew capsule to return astronauts to the moon later this decade.
Human muscle cells to be launched into space for aging research
Tiny human muscle cells will be blasted into space in an experiment that could help people live longer, healthier lives.
The experiment, called MicroAge, is set to be launched to the International Space Station (ISS) on Tuesday.
Space will be used to understand what happens to human muscles as people age, and why.
Lab-grown human muscle cells, the size of a grain of rice, have been put into small 3D-printed holders the size of a pencil sharpener.
Once in space, they will be electrically stimulated to induce contractions in the muscle tissue, and the scientists will look closely to see what happens.
Spending time without the effects of gravity can cause astronauts' muscles to get weaker, just as they do in older age, before recovering when they return to Earth.
University of Liverpool researchers, funded by the UK Space Agency, will study what happens to muscle tissue in space, and compare the findings to what happens on Earth.
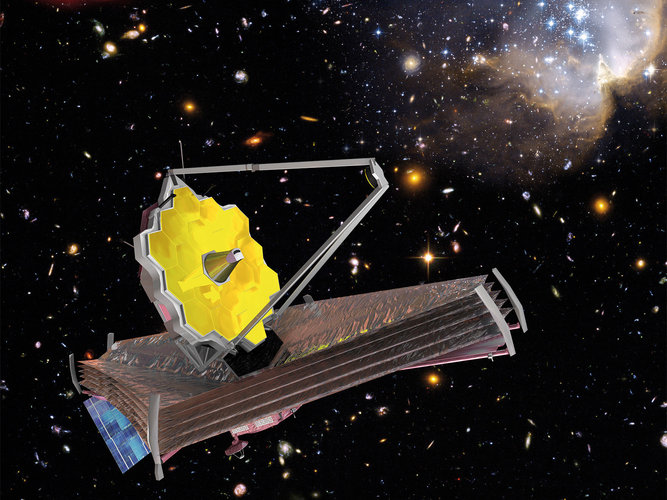
ESA catches Webb's first call
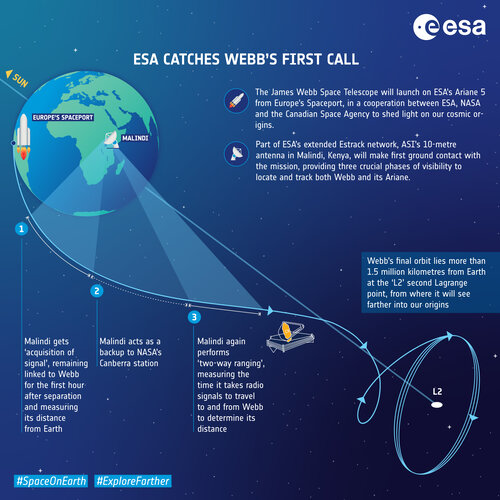 Image:
Image:
Webb is due to launch on an Ariane 5 rocket from Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana, at the earliest on 24 December. It will journey on a direct escape trajectory towards its target orbit more than 1.5 million kilometres from Earth. Part of ESA’s Estrack cooperative network, the 10-metre antenna in Malindi, Kenya, will make first contact from the ground with the fledgling mission, with the all-important ‘first acquisition of signal’.
About 23 minutes after lift-off, Malindi will locate the Ariane 5 launch vehicle in flight, rising above the Western horizon, still housing its precious cargo. Only five minutes later,
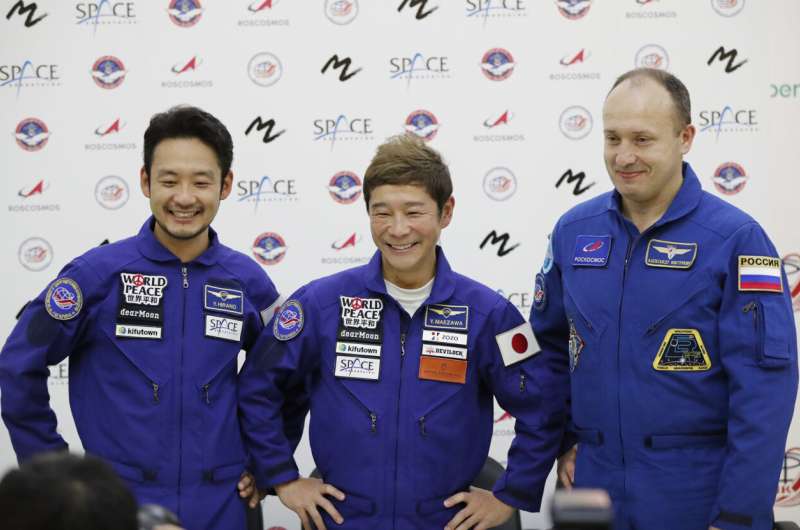
Japanese space tourists safely return to Earth

Secure Spanish satellites start construction
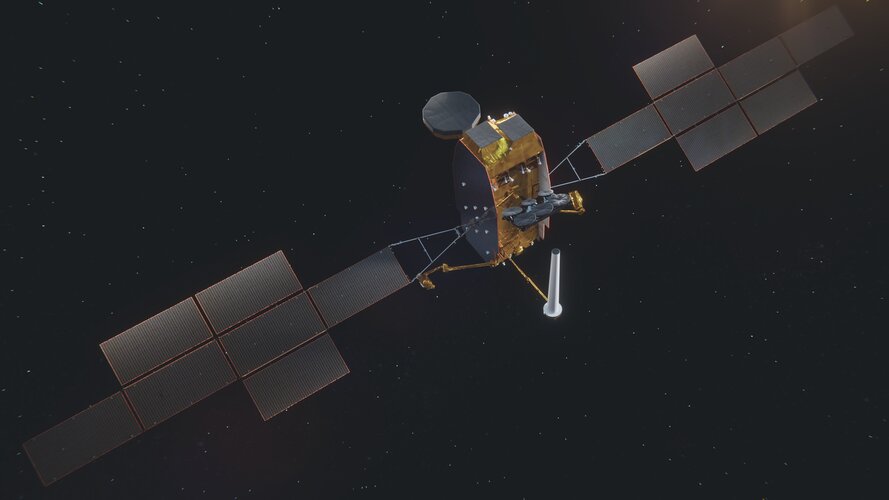

Two telecommunications satellites that can be reprogrammed while in space to respond to changing demands on Earth have passed their critical design reviews.
Dragon delivery – European science destined for space
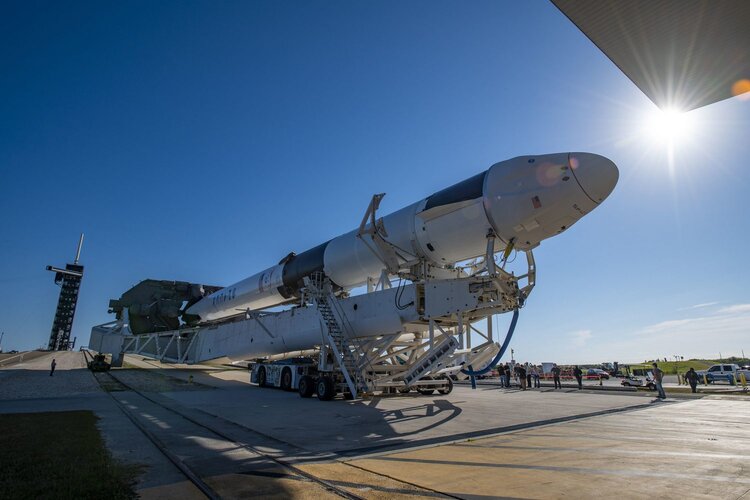

The next SpaceX resupply vehicle is packed with European science, ready for delivery to the International Space Station just in time for Christmas.
Japanese space tourists return to Earth after 12 days on ISS
 A Japanese billionaire returned to Earth Monday, after 12 days spent on the International Space Station where he made videos about performing mundane tasks in space including brushing teeth and going to the bathroom.
Online fashion tycoon Yusaku Maezawa and his assistant Yozo Hirano parachuted onto Kazakhstan's steppe at around the expected landing time of 0313 GMT Monday, along with Russia
A Japanese billionaire returned to Earth Monday, after 12 days spent on the International Space Station where he made videos about performing mundane tasks in space including brushing teeth and going to the bathroom.
Online fashion tycoon Yusaku Maezawa and his assistant Yozo Hirano parachuted onto Kazakhstan's steppe at around the expected landing time of 0313 GMT Monday, along with Russia 
