
Copernical Team
NASA's X-59 Calls on Texas for Key Testing
 It appears the road to enabling a future that includes convenient commercial supersonic air travel over land demands a substantial pit stop in Fort Worth, Texas.
Who knew?
Aeronautical innovators at NASA and Lockheed Martin did. They have long planned for this milestone in assembling and testing the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology (QueSST) airplane.
Although the X-59 QueSST is
It appears the road to enabling a future that includes convenient commercial supersonic air travel over land demands a substantial pit stop in Fort Worth, Texas.
Who knew?
Aeronautical innovators at NASA and Lockheed Martin did. They have long planned for this milestone in assembling and testing the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology (QueSST) airplane.
Although the X-59 QueSST is China hits back at US after satellite near-misses
 China has stated the United States is in no position to unilaterally set thresholds for emergency collision after the US rejected the charge its Starlink satellites endangered China's space station.
Foreign Ministry spokesman Zhao Lijian made the remarks at a daily news briefing on Thursday, saying such rhetoric by the US did not show a responsible attitude as a major country strong in aer
China has stated the United States is in no position to unilaterally set thresholds for emergency collision after the US rejected the charge its Starlink satellites endangered China's space station.
Foreign Ministry spokesman Zhao Lijian made the remarks at a daily news briefing on Thursday, saying such rhetoric by the US did not show a responsible attitude as a major country strong in aer Mars rover Perseverance notches a year of science, tech achievements
 The Mars rover Perseverance and its feisty sidekick helicopter Ingenuity have set records and pushed new frontiers for interplanetary space exploration since landing on the Red Planet one year ago this Friday.
The flawless landing of the rover in Mars' Jezero Crater, on Feb. 18, 2021, kicked off a year of successes, including the first rock sample drilled on another planet, the first ti
The Mars rover Perseverance and its feisty sidekick helicopter Ingenuity have set records and pushed new frontiers for interplanetary space exploration since landing on the Red Planet one year ago this Friday.
The flawless landing of the rover in Mars' Jezero Crater, on Feb. 18, 2021, kicked off a year of successes, including the first rock sample drilled on another planet, the first ti SpaceX plans new private spaceflight missions, first private spacewalk
 SpaceX plans to launch a new private astronaut mission, Polaris Dawn, from Florida as early as Nov. 1 and will attempt to conduct the first private spacewalk in history, the company announced Monday.
Businessman Jared Isaacman, founder and CEO of the payments company Shift4, will command the mission, having previously he led the first all-private orbital mission in September known as In
SpaceX plans to launch a new private astronaut mission, Polaris Dawn, from Florida as early as Nov. 1 and will attempt to conduct the first private spacewalk in history, the company announced Monday.
Businessman Jared Isaacman, founder and CEO of the payments company Shift4, will command the mission, having previously he led the first all-private orbital mission in September known as In Rocket set to hit Moon was built by China, not SpaceX, say astronomers
 Astronomy experts say they originally misread the secrets of the night sky last month: it turns out that a rocket expected to crash into the Moon in early March was built by China, not SpaceX.
A rocket will indeed strike the lunar surface on March 4, but contrary to what had been announced, it was built not by Elon Musk's company, but by Beijing, experts now say.
The rocket is now said t
Astronomy experts say they originally misread the secrets of the night sky last month: it turns out that a rocket expected to crash into the Moon in early March was built by China, not SpaceX.
A rocket will indeed strike the lunar surface on March 4, but contrary to what had been announced, it was built not by Elon Musk's company, but by Beijing, experts now say.
The rocket is now said t US billionaire announces three more ambitious SpaceX flights
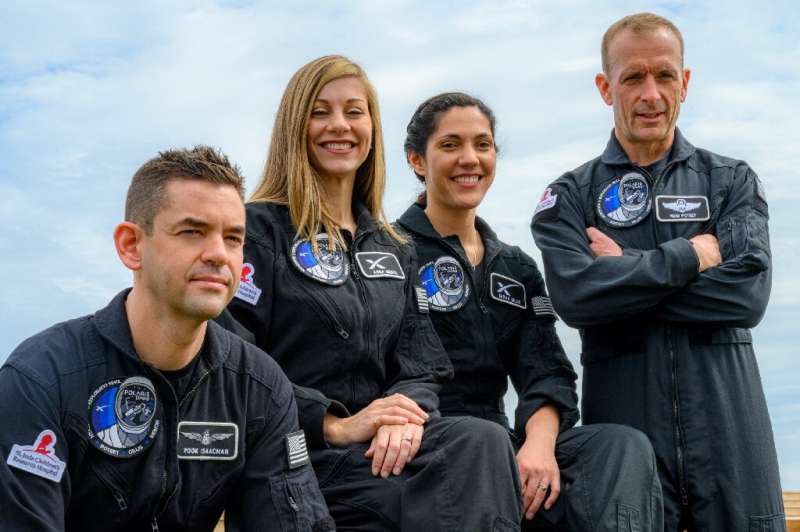

US billionaire Jared Isaacman, who chartered the first all-civilian orbital spaceflight, announced Monday three more private missions with SpaceX—which will include spacewalking and culminate in the first crewed flight of the next-generation Starship rocket.
The first, named Polaris Dawn, will take place no sooner than the fourth quarter of this year, and will be commanded by Isaacman, the founder of payment processing company Shift4.
The program represents a new step for the commercial space sector, as Elon Musk's SpaceX seeks to carry out more ambitious missions that were until now the domain of national space agencies.
In a press call, Isaacman revealed that the Polaris Program, named after the North Star, will be co-funded by himself and SpaceX. He declined to give further details such as total cost, or the percentage each side would contribute.
Materials science in motion | Cosmic Kiss
 Video:
00:02:01
Video:
00:02:01
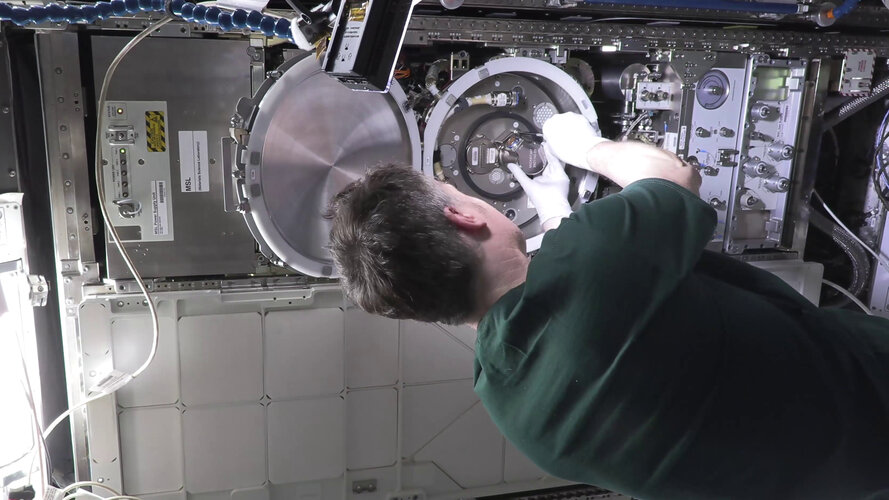
Watch ESA astronaut Matthias Maurer exchange a sample in the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) on the International Space Station.
The sample is for an experiment called MICAST that aims to deepen our understanding of the physical principles that govern solidification processes in metal alloys. This knowledge could help improve casting processes on Earth, leading to the development of new lightweight, high-performance materials for future spacecraft and innovation.
Matthias is spending approximately six months aboard the Space Station for his ESA mission Cosmic Kiss. During this time, he will support around 36 European and many more international experiments in orbit.
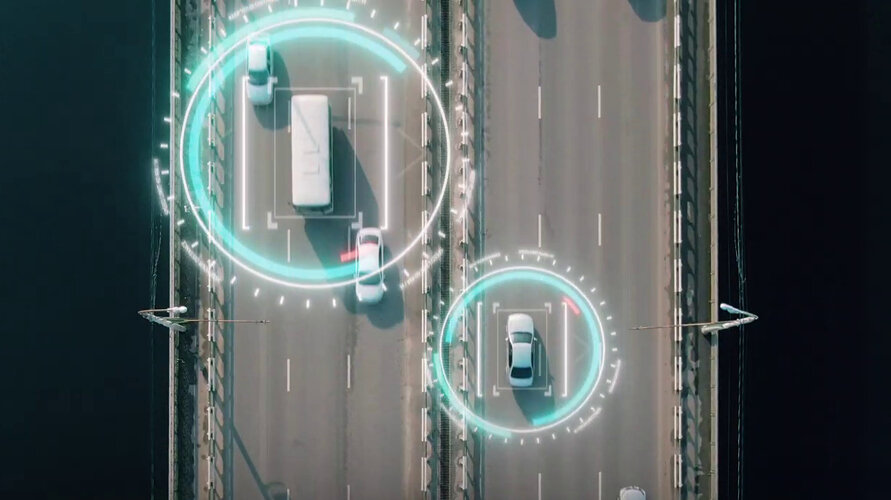
Inventing the future of Navigation
 Video:
00:05:15
Video:
00:05:15
Many of the experts that designed and oversaw the Galileo satnav system are now supporting cutting-edge European companies in the development of new navigation technologies and services. The result is ESA’s Navigation Innovation and Support Programme, NAVISP.
NAVISP is looking into all kinds of clever ideas about the future of navigation: ways to improve satellite navigation, alternative positioning systems and, new navigation services and applications. Working in partnership with European industry and researchers, more than 200 NAVISP projects have been initiated so far.
NAVISP is divided into three elements, the first looking into improving and expanding
Musk shows how they're planning to catch SuperHeavy boosters
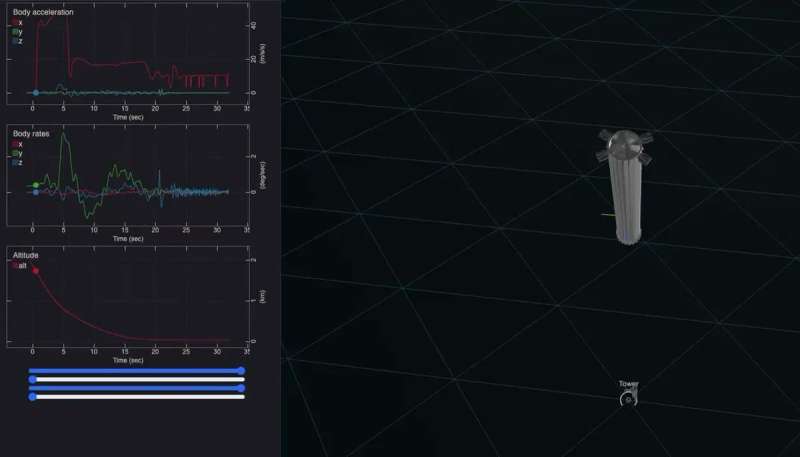
SpaceX's entire business model is based on the reusability of its rockets. That business model has proven viable time and time again as boosters continue to land safely only to be reused later. But as the rockets they're using get bigger and bigger, the harder and harder it will get for them to land directly on the ground, as models they've completed so far have. So for its SuperHeavy Booster, designed to launch its Starship craft into orbit, SpaceX has to develop a new way of capturing the rockets without damaging them. Its head, Elon Musk, has shared a Twitter video showing how it will do just that.
The video, which is only 24 seconds long, shows a computer simulation of a SuperHeavy Booster descending back to Earth after launching its payload into orbit. It's been viewed 4.3 million times as of the time of writing and has prompted a firestorm of interest online.
SpaceX, Virgin Orbit and Ferrari join ESA-NASA Advanced Manufacturing event

Confirmed speakers at next month’s ESA-NASA 1st International Conference on Advanced Manufacturing for Air, Space and Land Transportation include leading technologists from Airbus, Boeing, SpaceX, Virgin Orbit and Ferrari’s Formula 1 team. Registration is now open for the four-day online event, which will include more than 185 speakers from the scientific and engineering communities.
