
Copernical Team
Webb reveals steamy atmosphere of distant planet in exquisite detail
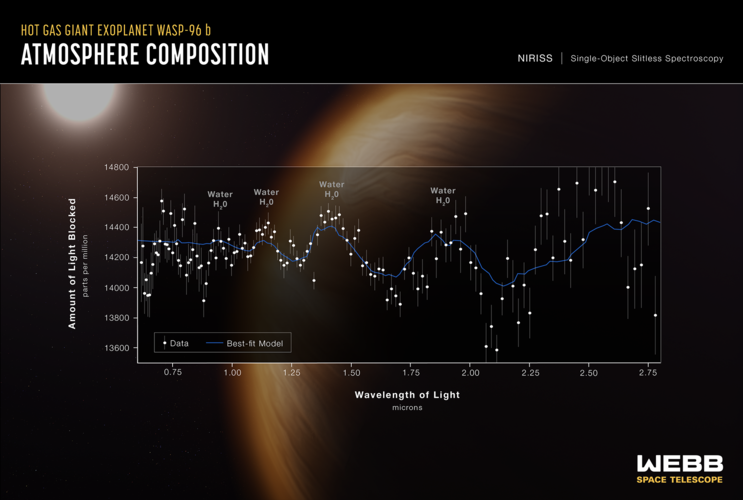
Webb’s enormous mirror and precise instruments joined forces to capture the most detailed measurements of starlight filtering through the atmosphere of a planet outside our Solar System to date.
The spectrum of light – which contains information about the makeup of a planetary atmosphere 1,150 light-years away – reveals the distinct signature of water. The strength of the signal that Webb detected hints at the significant role the telescope will play in the search for potentially habitable planets in the coming years. Webb’s powerful new view also shows evidence of haze and clouds that previous studies
Webb captures dying star’s final ‘performance’ in fine detail
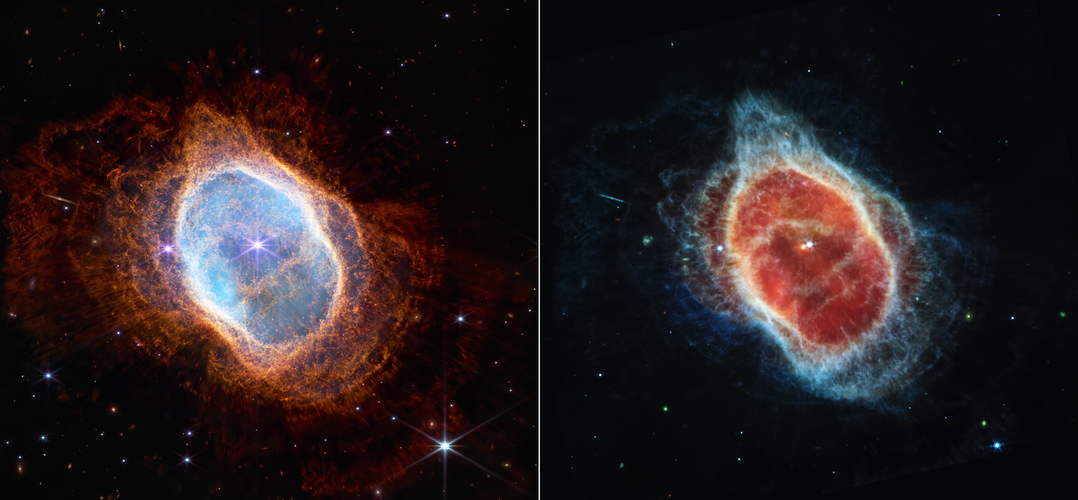

The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope has revealed details of the Southern Ring planetary nebula that were previously hidden from astronomers.
Webb sheds light on galaxy evolution, black holes
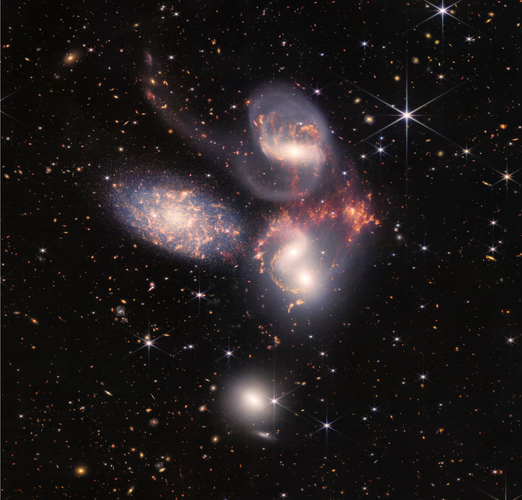

In this enormous new image, the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope reveals never-before-seen details of the galaxy group “Stephan’s Quintet”.
Close proximity of the system gives astronomers a ringside seat to galactic mergers and interactions. Webb’s new image also shows in rare detail how interacting galaxies trigger star formation in each other and how gas in galaxies is being disturbed and the outflows driven by a black hole in Stephan’s Quintet in a level of detail never seen before. Tight galaxy groups like this may have been more common in the early Universe when superheated, infalling
First images from Webb telescope reveal unseen Universe
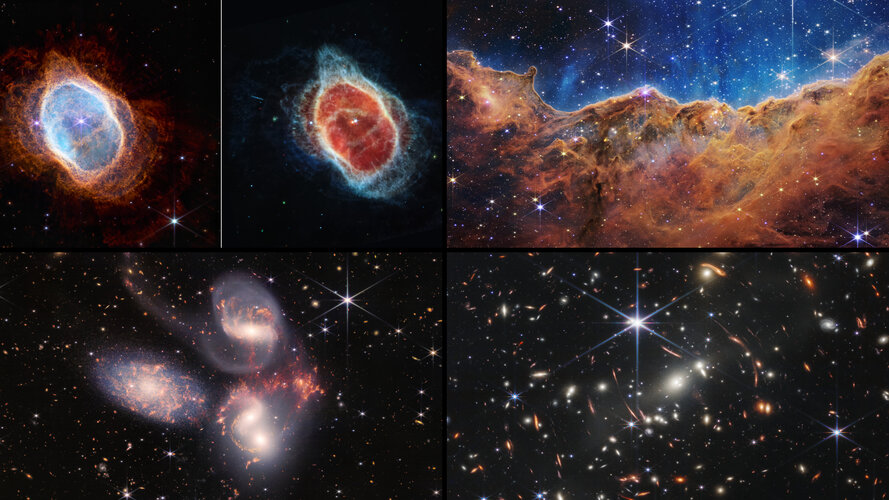

Highly anticipated observations hint at treasure trove of discoveries to come
The dawn of a new era in astronomy has begun as the world gets its first look at the full capabilities of the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope. The telescope’s first full-colour images and spectroscopic data, which uncover a spectacular collection of cosmic features that have remained elusive until now, were released today.
Webb reveals “Cosmic Cliffs” – a glittering landscape of star birth
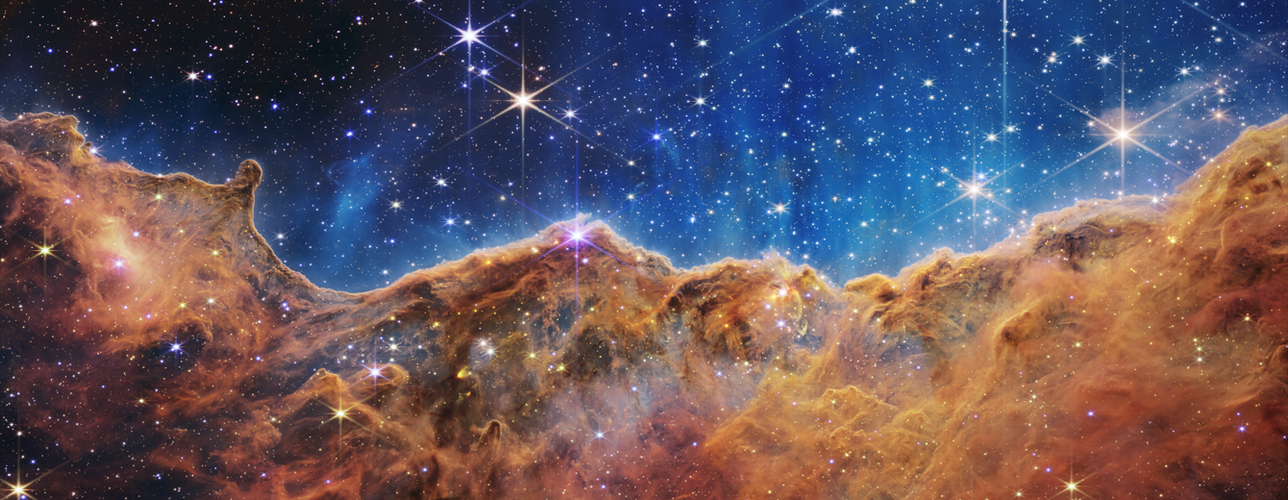

The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope reveals emerging stellar nurseries and individual stars in Carina Nebula that were previously obscured.
The new images showcase how Webb’s cameras can peer through cosmic dust, shedding new light on how stars form. Objects in earliest, rapid phases of star formation difficult to capture, but Webb’s extreme sensitivity, spatial resolution, and imaging capability can chronicle these elusive events.
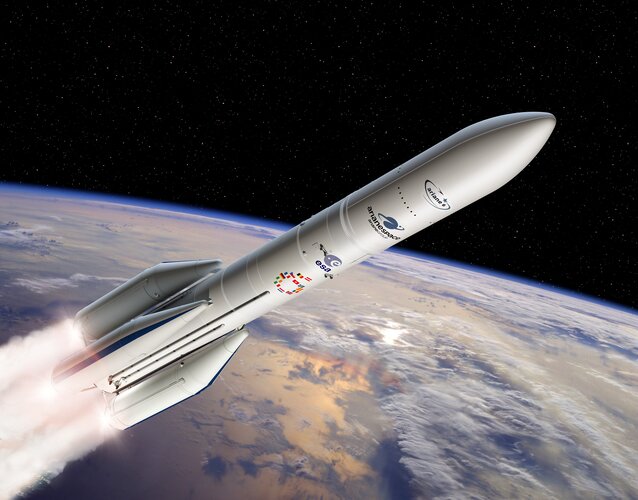
Vega-C: watch tomorrow's launch

ESA’s new Vega-C rocket is just one day from its inaugural flight. You can follow live on ESA Web TV. Flight VV21 will lift off as soon as 13 July at 13:13 CEST, pending suitable conditions for launch.
Broadcast begins 12:45 CEST/11:45 BST on ESA Web TV
13:13 CEST/12:13 BST/11:13 UTC/08:13 Kourou – liftoff
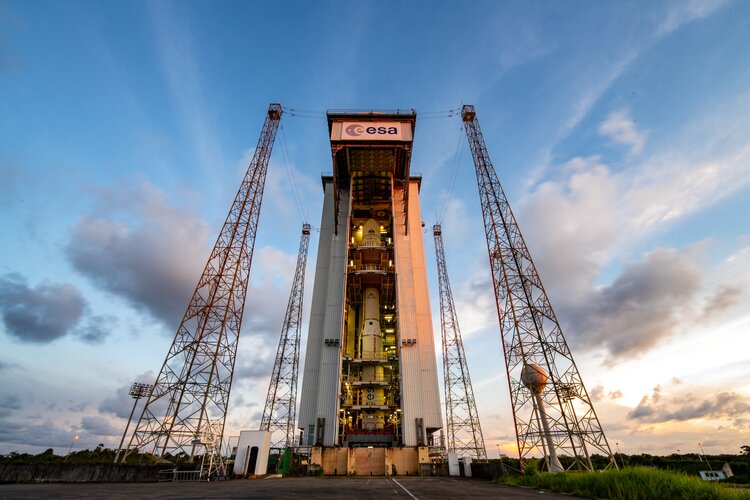
Ariane 6 central core transferred to mobile gantry

The Ariane 6 launch pad at Europe’s Spaceport in French Guiana now hosts the first example of ESA’s new heavy-lift rocket. This Ariane 6 combined tests model will be used to validate the entire launch system during its ground phase in readiness for the inaugural launch of Ariane 6.
AI CubeSat headed to Van Allen Belts on Vega-C

An ESA-financed nanosatellite, due to lift off aboard the inaugural flight of Vega-C this Wednesday, will operate an AI system in the harsh, radiation-wracked environment of the Van Allen Belts. The shoebox-sized Trisat-R – one of six ‘CubeSats’ on the flight, headed up to a rarely-trafficked close to 6000 km altitude orbit – is also carrying radiation-detection payloads from CERN, the European Council for Nuclear Research, Slovenian firm SkyLabs and ESA itself.
Upside-down design expands wide-spectrum super-camera abilities
 By turning a traditional lab-based fabrication process upside down, researchers at Duke University have greatly expanded the abilities of light-manipulating metasurfaces while also making them much more robust against the elements.
The combination could allow these quickly maturing devices to be used in a wide range of practical applications, such as cameras that capture images in a broad
By turning a traditional lab-based fabrication process upside down, researchers at Duke University have greatly expanded the abilities of light-manipulating metasurfaces while also making them much more robust against the elements.
The combination could allow these quickly maturing devices to be used in a wide range of practical applications, such as cameras that capture images in a broad Virgin Galactic picks Boeing subsidiary to build two motherships
 Space travel company Virgin Galactic on Wednesday said it had reached an agreement with Boeing subsidiary Aurora Flight Sciences to build two new air launch carrier aircraft for its spaceships.
These new "motherships" will replace Virgin Galactic's existing carrier plane - the VMS Eve built by Scaled Composites - with the first of the new aircraft due to enter service by 2025. The company
Space travel company Virgin Galactic on Wednesday said it had reached an agreement with Boeing subsidiary Aurora Flight Sciences to build two new air launch carrier aircraft for its spaceships.
These new "motherships" will replace Virgin Galactic's existing carrier plane - the VMS Eve built by Scaled Composites - with the first of the new aircraft due to enter service by 2025. The company 