
Copernical Team
Space telescope tracing dark energy to be launched July 1
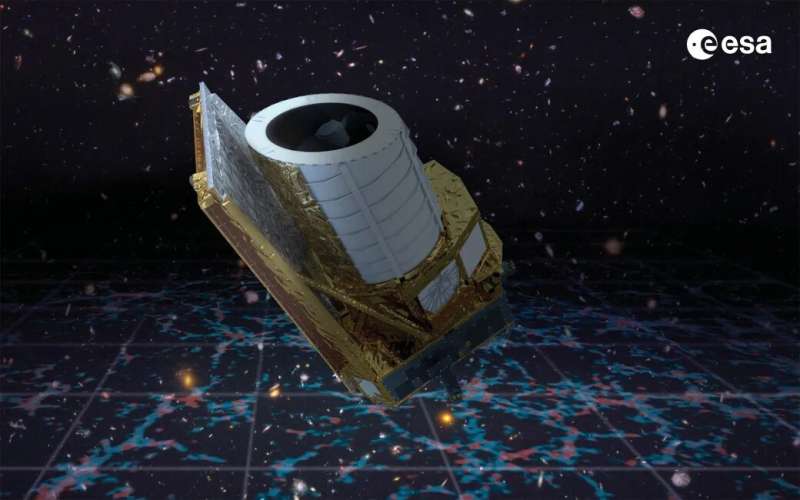

The Euclid space telescope has a target launch date of July 1, 2023 (18:11 Finnish time at the earliest) with a backup launch date of July 2, 2023.
In six years, Euclid will complete a task that would take older telescopes like Hubble or Webb over a century. The main objective is to solve the problem of dark energy, i.e., why has the expansion of the universe started to accelerate?
A map to reveal the secrets of dark matter and dark energy
Europe's Euclid space telescope to launch on July 1
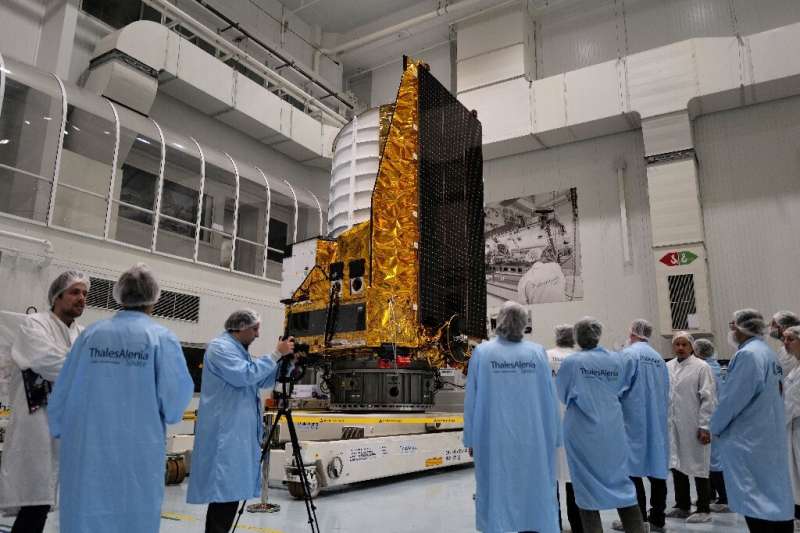

The European Space Agency said on Wednesday its space telescope Euclid is scheduled to launch on July 1, blasting off on a mission to shed light on the mysteries of dark matter and dark energy.
The mission will launch on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral in Florida, with the broadcast beginning at 1430 GMT, the ESA said in a tweet.
Euclid was originally planned to ride into space on a Russian Soyuz rocket, but last year Moscow withdrew its launchers in response to sanctions over the invasion of Ukraine.
The ESA was forced to turn to its rival SpaceX, the US company of billionaire Elon Musk, to launch the 1.4-billion-euro ($1.5 billion) mission.
Detecting and estimating satellite maneuvers more accurately
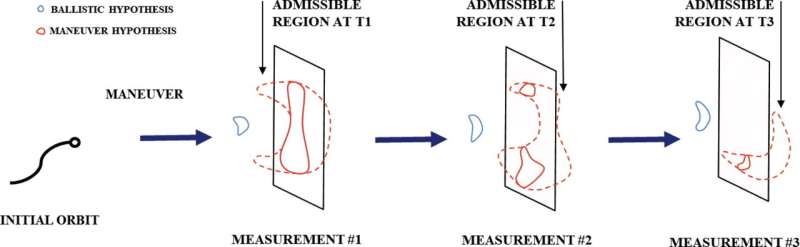
Researchers from the Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M), Polytechnic University of Milan and the company GMV have developed a new methodology for detecting and estimating satellite maneuvers that improves the operation of the systems currently in use. This development, which is already being tested in operational environments, may help reduce the problem of space debris.
The number of satellites and fragments of space debris in Earth orbit currently amounts to around 30,000, according to the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA catalogs, although researchers in this field estimate the real number to be around 100,000.
A trio of images highlight BepiColombo's third Mercury flyby
 The ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission has made its third of six gravity assist flybys at Mercury, snapping images of a newly named impact crater as well as tectonic and volcanic curiosities as it adjusts its trajectory for entering Mercury orbit in 2025.
The closest approach took place at 19:34 UTC (21:34 CEST) on 19 June 2023, about 236 km above the planet's surface, on the night side of the p
The ESA/JAXA BepiColombo mission has made its third of six gravity assist flybys at Mercury, snapping images of a newly named impact crater as well as tectonic and volcanic curiosities as it adjusts its trajectory for entering Mercury orbit in 2025.
The closest approach took place at 19:34 UTC (21:34 CEST) on 19 June 2023, about 236 km above the planet's surface, on the night side of the p Paris Air Show 2023 in pictures – Day 3

We are almost halfway through the week of the 54th edition of the Paris Air Show.
ESA is taking part with an exhibition in the Space Pavilion alongside with CNES, the French National Space Agency. Throughout the week, the pavilion will host presentations, events and temporary exhibitions from both agencies, while several events will be held in the ESA/CNES shared area.
Click the link here to view the full programme of events being held in the ESA-CNES shared area.
Here below the photo highlights of Day n.3 from Le Bourget Airport. The event will take place from 19 to 25 June.
Paris Air Show Live - Press briefing on Space Transportation
 Video:
00:40:18
Video:
00:40:18
Watch the replay of the press briefing on space transportation from Paris Air Show 2023. Speakers will share the current status of the Ariane 6 programme, and the next key milestones towards the inaugural flight.
ESA and CNES sign contract to maintain Spaceport, furthering modernisation and environmental sustainability
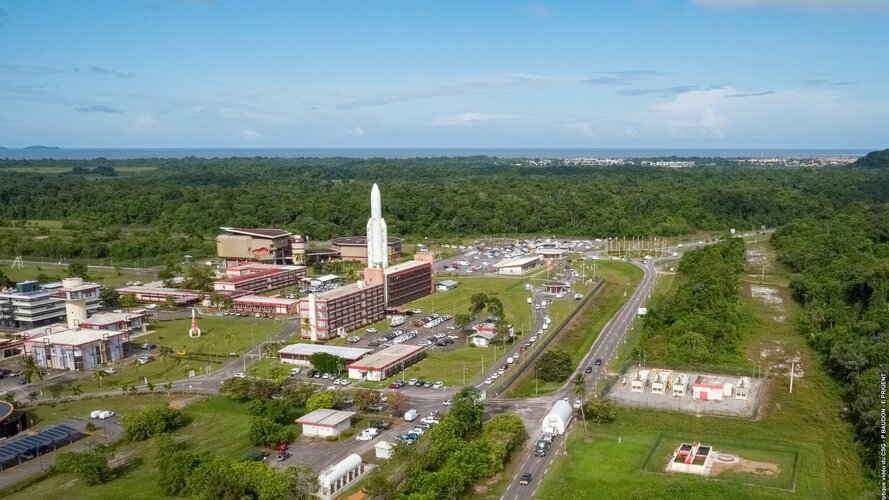

At the Paris air show today, ESA Director of Space Transportation Daniel Neuenschwander and CNES's Guiana Space Centre Director Marie-Anne Clair signed a contract, maintaining ESA’s role and focusing on objectives including improving flexibility to handle new payloads, reducing carbon footprint and furthering the digital transformation at Europe’s Spaceport to 2027. Looking on were ESA Director General Josef Aschbacher and CNES Deputy Chief Executive Lionel Suchet.
CNES has overall responsibility for maintaining the operational condition of the spaceport and modernizing facilities.
Paris Air Show live - From Earth science to climate action
Paris Air Show live: From Earth science to climate action
22 June at 12:00 CEST: Earth's water and carbon cycles from space
Industry invited to bid for low-Earth orbit satnav demo
Europe’s Galileo constellation is already the world’s most accurate satellite navigation system, providing metre-level precision to users worldwide. The general expectation is that satnav is going to keep on getting better, in line with increasing user needs and accuracy requirements. But in fact, traditional Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) in medium Earth orbit are approaching their limits of technical performance.
Iridium proposes a new model for monitored BVLOS UAS integration
 Iridium Communications Inc. (NASDAQ: IRDM) has announced the results of an Uncrewed Aircraft System (UAS) flight trial highlighting Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) capabilities in the National Airspace System (NAS), with a published a whitepaper titled "Monitored BVLOS: A New Model for UAS Integration in the National Airspace System." The whitepaper highlights and solves for challenges faced
Iridium Communications Inc. (NASDAQ: IRDM) has announced the results of an Uncrewed Aircraft System (UAS) flight trial highlighting Beyond Visual Line of Sight (BVLOS) capabilities in the National Airspace System (NAS), with a published a whitepaper titled "Monitored BVLOS: A New Model for UAS Integration in the National Airspace System." The whitepaper highlights and solves for challenges faced 