Environmental Research Letters
Rain-fed pulses of methane from East Africa during 2018–2019 contributed to atmospheric growth rate
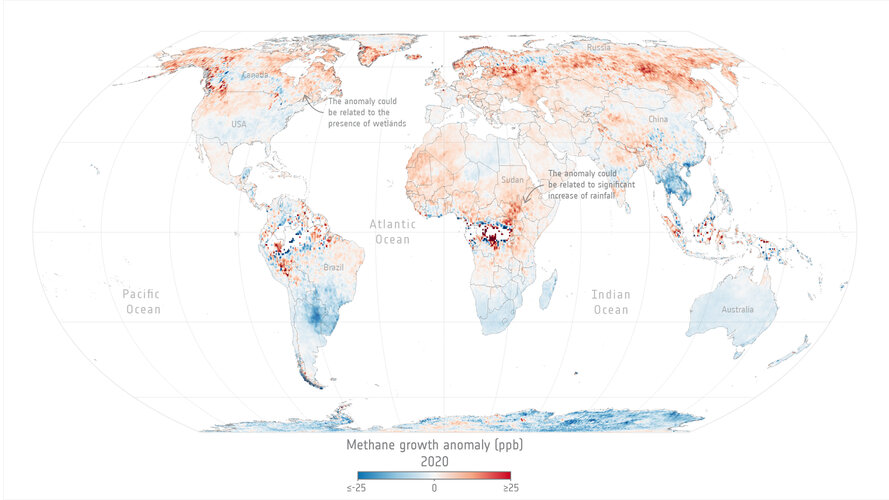
Levels of methane, the second most important greenhouse gas in our atmosphere, continued their unrelenting rise in 2020 despite the economic slowdown caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
A team of scientists, from the University of Leeds, have used data from the Copernicus Sentinel-5P satellite to pinpoint locations with large surges of methane emissions. These findings were presented during ESA’s Living Planet Symposium which took place last month in Bonn, Germany.
Rain-fed pulses of methane from East Africa during 2018–2019 contributed to atmospheric growth rate